33 LangChain Alternatives That Won't Leak Your Data (2026 Guide)
Looking for a secure alternative to LangChain? Compare 33 frameworks for building LLM applications with better data privacy, self-hosting options, and enterprise compliance.

LangChain pulls in 400+ transitive dependencies. Every chain you build routes data through third-party APIs by default. For teams handling financial records, patient data, or proprietary IP, that dependency surface is a compliance risk hiding in plain sight.
LangChain is fine for prototyping. But when data security becomes a hard requirement, not a nice-to-have, you need frameworks built with data control as a default, not an afterthought.
This list covers 33 alternatives organized by security posture and use case. Every entry includes honest trade-offs pulled from real user feedback.
Why Developers Look for Secure LangChain Alternatives
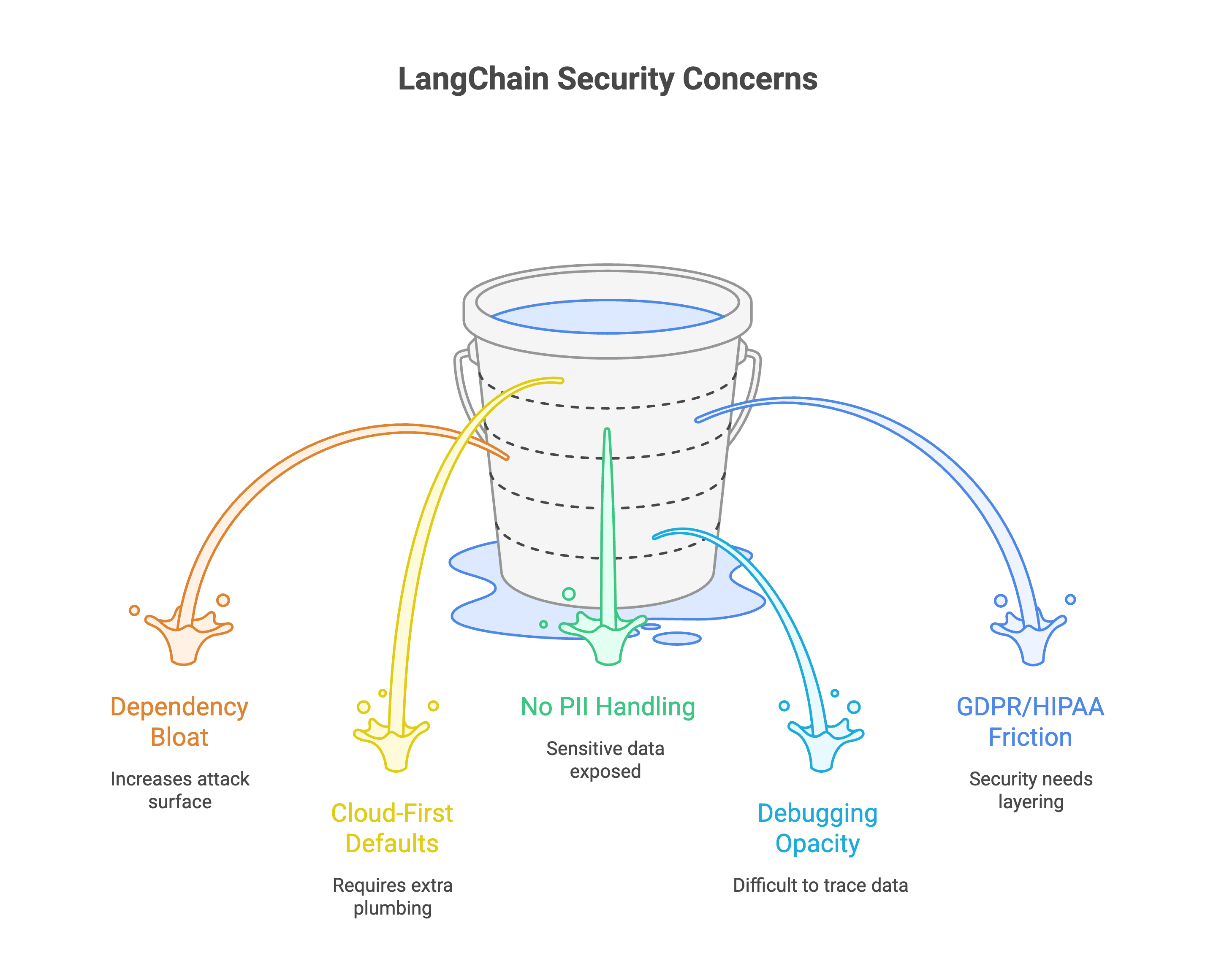
Five specific problems keep pushing teams away from LangChain in production:
Dependency bloat means attack surface. LangChain's package tree spans hundreds of transitive dependencies. Each one is a potential CVE waiting to surface. A single vulnerable sub-dependency can compromise your entire pipeline.
Cloud-first defaults. Most LangChain integrations assume you're shipping data to OpenAI, Pinecone, or another SaaS endpoint. Running everything on your own infrastructure requires extra plumbing that the framework doesn't make easy.
No built-in PII handling. LangChain's privacy tools (like the Amazon Comprehend chain) exist as optional add-ons. Nothing stops sensitive data from hitting an external API unless you bolt on protections yourself.
Debugging opacity. When a chain fails mid-execution, tracing exactly which data went where is difficult. If your compliance team needs audit trails, you're building that visibility from scratch. Worth noting: a LangSmith vulnerability in June 2025 could expose API keys via malicious agents.
GDPR and HIPAA friction. Building compliant applications with LangChain means layering security on top of a framework that wasn't designed for it. For teams dealing with RAG privacy concerns, that's a structural problem.
Enterprise AI Platforms (Built-in Compliance and Governance)
1. Prem AI
Swiss-based applied AI research lab offering a complete platform for building, fine-tuning, and deploying custom AI models. The architecture is stateless with zero data retention, and every interaction gets cryptographic verification. Built-in PII redaction handles sensitive data before it touches any model.
Security edge over LangChain: FADP, GDPR, and HIPAA compliant by default with hardware-signed attestations for privacy auditing. No data ever leaves your control boundary.
Best for: Enterprises needing full AI sovereignty with fine-tuning
Trade-offs: Pricing isn't publicly listed, so you'll need to contact sales for quotes. The platform is newer compared to established hyperscaler offerings, which means a smaller community for troubleshooting edge cases.
Some links - Prem Studio | Enterprise fine-tuning guide | Save 90% on LLM costs
2. IBM watsonx
Enterprise AI platform with a full compliance suite covering SOC2, HIPAA, and industry-specific regulations. Offers model governance, bias detection, and lifecycle management. Deep integration with IBM's existing enterprise stack.
Security edge over LangChain: End-to-end model governance with audit trails, data lineage tracking, and role-based access controls baked into the platform.
Best for: Regulated industries already running IBM infrastructure
Trade-offs: Heavy vendor lock-in once you're deep into the IBM ecosystem. Pricing is complex and significantly higher than open-source alternatives, which makes experimentation expensive.
3. Amazon Bedrock Agents
Managed agent orchestration within AWS. Data stays inside your VPC. IAM controls govern who accesses what. No data sharing between AWS accounts. Supports multiple foundation models through a single API.
Security edge over LangChain: Full VPC isolation with AWS IAM, KMS encryption, and PrivateLink support. Your data never crosses account boundaries.
Best for: Teams already in AWS needing managed agent orchestration
Trade-offs: Zero portability outside AWS. If you ever want to move to another cloud or on-premise, you're rewriting significant parts of your stack. Bedrock's agent capabilities are also less flexible than code-first frameworks for custom workflows.
4. Google Vertex AI Agent Builder
Google Cloud's agent platform with VPC Service Controls and Customer-Managed Encryption Keys (CMEK). Supports grounding agents with enterprise data through Search and Conversation APIs.
Security edge over LangChain: VPC Service Controls create a security perimeter around AI resources. CMEK gives you control over encryption keys rather than trusting the provider.
Best for: Google Cloud teams building grounded AI agents
Trade-offs: Locked into the Google ecosystem. Vertex AI's agent tooling changes frequently, and documentation sometimes lags behind feature releases. Less mature than Bedrock for agent-specific workflows.
5. Microsoft Semantic Kernel
Open-source SDK supporting Python and C#, with native Azure AD integration. Organizes AI capabilities into "skills" (prompt-based and code-based functions) that can be orchestrated by planners. Microsoft is actively merging it with AutoGen into the new Microsoft Agent Framework.
Security edge over LangChain: Native Azure AD and RBAC integration. Enterprise auth patterns feel familiar to Microsoft shops, and the SDK is designed for on-premise deployment behind corporate firewalls.
Best for: .NET teams building AI agents with enterprise auth
Trade-offs: The Python experience is noticeably behind the .NET side in stability and documentation. Multiple GitHub discussions show users confused about Semantic Kernel's future direction as Microsoft merges it with AutoGen. One thread had enterprise teams asking "is now the time to look for alternatives?" after mixed signals about deprecation. The API surface also changes frequently between releases.
6. Azure AI Agent Service
Managed agent hosting within Azure's compliance boundary. Integrates with Azure AI Foundry for model access and evaluation. Supports OpenAI Assistants API and custom models.
Security edge over LangChain: Inherits Azure's compliance certifications (SOC2, HIPAA, FedRAMP). Data stays within Azure's managed infrastructure with full encryption at rest and in transit.
Best for: Enterprises with existing Microsoft EA agreements
Trade-offs: Limited to Azure infrastructure only. The service is relatively new and still evolving, which means some features are in preview and not production-ready. Pricing can escalate quickly with heavy agent usage.
Privacy-First and Self-Hosted Frameworks
7. Haystack (deepset)
German-built, open-source framework designed for production RAG and search systems. Pipeline-based architecture lets you compose retrieval, generation, and evaluation steps. Full self-hosting support with no mandatory cloud dependencies. Haystack 2.x is a clean rewrite with a modular component system.
Security edge over LangChain: Built by a German company with GDPR alignment baked into the architecture. Every component can run on your own servers with no external API calls required.
Best for: Production RAG systems with European data residency needs
Trade-offs: The migration from Haystack 1.x to 2.x caused real confusion. A GitHub discussion shows users stuck between haystack-ai and farm-haystack packages, unable to use Agent features across versions. G2 reviewers also flag a steep learning curve and note that "difficult learning curve" and "slow performance due to reliance on Elasticsearch" are recurring pain points. Thread safety issues in multi-threaded production environments have surfaced on GitHub as well.
8. LlamaIndex
Data-first framework optimized for indexing and retrieving structured and unstructured data. Strong control over which data connects to which LLM endpoint. Offers hybrid search combining vector and keyword retrieval, plus built-in evaluation tools.
Security edge over LangChain: Data stays local during indexing. You control exactly which data reaches external LLMs, and the framework doesn't assume cloud-first defaults.
Best for: RAG pipelines where data governance matters
Trade-offs: A GitHub issue shows users reporting query times of "20-30 minutes to bring back a response" even on small documents. SelectHub reviews note "limited workflow flexibility" compared to LangChain, and "implementing advanced RAG techniques might require a steep learning curve, despite the framework's user-friendly reputation." Agent orchestration capabilities are less developed than dedicated agent frameworks.
9. PrivateGPT
Fully offline RAG system. No data leaves your machine. Supports local model inference through Ollama, llama.cpp, and other backends. Designed specifically for air-gapped environments where network isolation is mandatory.
Security edge over LangChain: Complete air-gap capability. Zero network calls, zero telemetry, zero external dependencies during inference.
Best for: Air-gapped environments and classified document analysis
Trade-offs: Limited to whatever models you can run locally, which means smaller, less capable models on typical hardware. No cloud scaling option, so throughput is capped by your local compute. The project moves slowly compared to faster-moving frameworks.
10. Ollama
Local model inference engine with zero network calls. Simple CLI interface for downloading and running open-source models. Supports GPU acceleration, quantized models, and an OpenAI-compatible API endpoint.
Security edge over LangChain: Inference happens entirely on-device. No data leaves your hardware. No telemetry, no API keys, no cloud dependency.
Best for: Developers wanting LLM access without data leaving the device
Trade-offs: Memory management is a real problem. GitHub issues document models failing to free memory after generation, eventually crashing the server. VRAM estimation is frequently inaccurate, with one report showing Ollama reporting memory as "almost unused" when over 1GB was consumed by other applications, causing runner crashes. Performance drops 5-20x when models overflow from GPU VRAM into system RAM. Also, Ollama is inference only. No orchestration, no pipelines, no agent logic.
Internal link: Self-hosted LLM guide
11. LocalAI
OpenAI-compatible API that runs entirely on your own hardware. Drop-in replacement for OpenAI's API endpoint. Supports text generation, embeddings, image generation, and speech-to-text, all locally.
Security edge over LangChain: API-compatible local inference means you can swap out cloud LLM calls for local ones without changing application code. No data touches external servers.
Best for: Drop-in LangChain replacement with local-only inference
Trade-offs: Performance is entirely dependent on your hardware. CPU-only inference on large models is painfully slow (3-6 tokens/second). Setup and model configuration can be fiddly compared to Ollama's one-command approach.
12. Jan.ai
Desktop-first application for running LLMs locally with full offline mode. Clean UI that makes local model management accessible to non-technical users. Supports multiple model formats and includes a built-in conversation interface.
Security edge over LangChain: Fully offline desktop application. Models and conversations stay on your machine with no cloud sync by default.
Best for: Individual developers needing a private AI assistant
Trade-offs: Not designed for multi-user production deployments. Single-user focus means no team collaboration features, no API-first architecture, and no built-in scaling path.
13. AnythingLLM
Self-hosted document chat platform with built-in user permissions and workspace management. Supports multiple LLM backends (OpenAI, Ollama, local models) and vector databases. Includes document processing, embedding, and retrieval in one package.
Security edge over LangChain: Complete self-hosting with multi-user access controls. Workspaces isolate data between teams. Supports fully local operation with Ollama backend.
Best for: Teams wanting a turnkey private RAG workspace
Trade-offs: Less customizable than code-first frameworks. If your use case doesn't fit the built-in UI patterns, you'll hit limitations quickly. The SMB focus means enterprise features like SSO and advanced audit logging are limited.
14. GPT4All
Runs open-source models locally on consumer hardware, including laptops without dedicated GPUs. Nomic AI backs the project with a focus on making local inference accessible. Includes a desktop chat interface and a Python SDK.
Security edge over LangChain: Everything runs locally on consumer hardware. No API keys, no cloud accounts, no data leaving your device.
Best for: Privacy-conscious teams running LLMs on a budget
Trade-offs: Model selection is more limited than cloud options. Performance on CPU-only machines is acceptable for short queries but frustrating for longer generation tasks. The SDK is simpler than full frameworks, so complex workflows need custom code.
Open-Source Agent Frameworks (With Security Controls)
15. CrewAI
Role-based agent orchestration framework where you define agents with specific roles, goals, and backstories. Agents collaborate on tasks through a structured workflow. Full self-hosting support with local model backends.
Security edge over LangChain: Self-hostable with local model support. Agent boundaries are explicit, so you can control which agents access which data sources.
Best for: Multi-agent workflows with defined access boundaries
Trade-offs: Trustpilot reviews flag privacy concerns: CrewAI "collects telemetry data without clear consent" and users report difficulty disabling it. A Towards Data Science analysis found that the "hierarchical manager-worker pattern doesn't work as documented" because the manager executes tasks sequentially instead of coordinating agents. G2 reviewers note "building complex agentic flows requires very much trial and error."
Checkout: Open-source agentic frameworks compared
16. AutoGen (Microsoft)
Multi-agent conversation framework with configurable code execution sandboxing. Agents communicate through messages and can be constrained by custom policies. Now being merged into the Microsoft Agent Framework alongside Semantic Kernel.
Security edge over LangChain: Code execution happens in sandboxed environments (Docker containers). Agent communication patterns can be restricted to prevent unauthorized data access.
Best for: Research and complex multi-agent systems with safety guardrails
Trade-offs: The AutoGen to Microsoft Agent Framework transition has left some users uncertain about the migration path. Still maturing for production use, with many features marked as experimental. Documentation can be sparse for advanced patterns.
17. LangGraph
Built on top of LangChain but adds stateful, graph-based workflow control. Enables cycles, branching, and persistence in agent workflows. LangGraph Studio provides visual debugging.
Security edge over LangChain: Adds state management and checkpointing, making audit trails more feasible than vanilla LangChain chains.
Best for: LangChain teams needing better workflow governance
Trade-offs: Still carries LangChain's entire dependency footprint, so the attack surface problem remains. The best debugging and observability features live on LangGraph Server (not the open-source library), pushing you toward LangSmith's paid platform. Reddit users frequently complain about breaking changes across LangChain 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3.
18. Griptape
Enterprise-focused agent framework with built-in guardrails for agent behavior. Structures agent actions through a "rules" system that constrains what agents can and cannot do. Supports both cloud and self-hosted deployment.
Security edge over LangChain: Policy enforcement is a first-class feature, not an afterthought. Agent behavior boundaries are defined declaratively before deployment.
Best for: Production agent systems needing policy enforcement
Trade-offs: Smaller community than LangChain or LlamaIndex. Finding help for edge cases often means going directly to the maintainers. Fewer pre-built integrations mean more custom connector work.
19. Langroid
Lightweight Python agent framework designed with minimal dependencies. Clean architecture using a message-passing pattern between agents. Focuses on simplicity over feature breadth.
Security edge over LangChain: Tiny dependency footprint means dramatically smaller attack surface. You can audit the entire codebase in a reasonable timeframe.
Best for: Teams wanting agent capabilities without dependency bloat
Trade-offs: Fewer integrations out of the box. If you need connectors for niche tools or vector databases, you're writing them yourself. Smaller community means less Stack Overflow help and fewer tutorials.
20. MetaGPT
Multi-agent framework where agents take on structured roles (product manager, architect, engineer) to collaborate on complex tasks. Enforces a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) pattern for agent coordination.
Security edge over LangChain: Role-based agent boundaries create natural data access controls. Each agent only sees data relevant to its defined role.
Best for: Complex agent collaborations with clear task boundaries
Trade-offs: The opinionated SOP architecture is great when it fits your use case but restrictive when it doesn't. Customizing the agent interaction patterns beyond the built-in roles requires significant effort. Less flexible than general-purpose orchestrators.
Minimal-Surface-Area LLM Libraries
21. DSPy (Stanford)
Programmatic prompt optimization framework from Stanford NLP. Replaces string-template prompting with compiled programs that optimize prompts automatically. Treats LLM interactions as typed, composable functions rather than ad-hoc chains.
Security edge over LangChain: Minimal dependency footprint. Programmatic control over exactly what data reaches the LLM, with no hidden chain abstractions sending data to unexpected places.
Best for: Teams wanting full control over what goes to the LLM
Trade-offs: The learning curve is steep. A Medium analysis describes "shortcomings with respect to concepts, documented examples, and lack of use cases." DSPy's own documentation acknowledges missing first-class observability, experiment tracking, and cost management. DataCamp notes the "need for substantial computational resources for large-scale optimization tasks." If your use case is simple, DSPy adds unnecessary complexity.
22. Mirascope
Thin Python wrapper around LLM APIs with minimal dependencies. Uses standard Python decorators and type hints rather than custom abstractions. Supports multiple LLM providers through a consistent interface.
Security edge over LangChain: Minimal abstraction layer means you see exactly what's being sent to each API. No hidden middleware or implicit data routing.
Best for: Python developers who prefer native code over framework magic
Trade-offs: You build more infrastructure yourself. No built-in RAG, no agent orchestration, no memory management. It's a calling layer, not a platform.
23. Instructor
Structured output extraction library built on Pydantic validation. Ensures LLM responses conform to typed schemas. Works with OpenAI, Anthropic, and other providers.
Security edge over LangChain: Single-purpose library with a tiny attack surface. Pydantic validation catches malformed outputs before they enter your application logic.
Best for: Getting reliable, typed data from LLMs with minimal code
Trade-offs: Single-purpose by design. Not an orchestration tool, not an agent framework, not a RAG system. You'll combine it with other libraries for anything beyond structured extraction.
24. Outlines (dottxt)
Constrained generation library using grammar-based sampling. Forces LLM outputs to follow specific formats (JSON schemas, regex patterns, context-free grammars). Works at the token level to guarantee structural correctness.
Security edge over LangChain: Output constraints prevent LLMs from generating unexpected data formats, reducing injection risks and data leakage through malformed responses.
Best for: Ensuring LLM outputs never contain unexpected data formats
Trade-offs: Focused entirely on output control. No workflow orchestration, no agent logic, no retrieval. Performance overhead from constrained sampling can increase latency on complex grammars.
25. LiteLLM
Unified API proxy for 100+ LLM providers with built-in rate limiting, budget controls, and access management. Acts as a gateway layer between your application and LLM APIs. Supports spend tracking per user, team, or project.
Security edge over LangChain: Centralizes LLM access through a single proxy with role-based permissions, budget limits, and usage monitoring. Makes it possible to audit every LLM call across your organization.
Best for: Managing LLM access across teams with spend controls
Trade-offs: Proxy layer only. Doesn't help you build applications. Adds a network hop to every LLM call, which increases latency. Self-hosting the proxy requires infrastructure management.
Low-Code and Visual Builders (Self-Hostable)
26. n8n
Open-source workflow automation platform with a visual builder and full self-hosting support. 400+ integrations including AI-specific nodes for LLMs, vector databases, and document processing. Active community with a large template library.
Security edge over LangChain: Self-hostable on your own infrastructure. Workflow execution stays within your network. Enterprise edition adds SSO and audit logging.
Best for: Non-developers building AI workflows on their own infrastructure
Trade-offs: AiX Society's review notes n8n "lacks native tools to compare prompt versions" or do LLM-specific monitoring. The visual builder means less fine-grained control over code execution. Usage-based pricing on the cloud version makes costs hard to predict at scale.
27. Flowise AI
Drag-and-drop LLM application builder with self-hosting support. Visual interface for composing RAG pipelines, chatbots, and agent workflows. Built on LangChain and LlamaIndex under the hood.
Security edge over LangChain: Self-hostable with Docker. The visual interface makes it easier to audit data flows than reading LangChain code.
Best for: Rapid prototyping with full infrastructure control
Trade-offs: An API2O review notes that "node configurations are always fully displayed, making complex workflows hard to view" as the canvas gets cluttered. The Agentflow feature is described as "still very incomplete, cannot meet prototype development" requirements for advanced use cases. Also, since it's built on LangChain underneath, you inherit LangChain's dependency footprint.
28. Dify
Open-source LLM application platform combining RAG, agents, and workflows in a single interface. Includes visual prompt engineering, dataset management, and API publishing. Active development with frequent releases.
Security edge over LangChain: Self-hostable with Docker Compose. Built-in dataset management keeps document processing within your infrastructure. API keys and model configurations stay server-side.
Best for: Teams wanting a self-hosted alternative to cloud AI platforms
Trade-offs: An API2O review flags that structured input and output "only supports 1-level depth member definitions," limiting complex nested data handling. Workflow features are still maturing. The project is newer than established frameworks, so expect some rough edges in production.
29. Rivet
Visual AI programming environment from Ironclad, open-source. Graph-based editor for composing and debugging LLM workflows. Strong focus on prompt iteration and testing.
Security edge over LangChain: Visual execution traces make it easy to see exactly what data flows where. Self-hostable with no cloud dependency.
Best for: Debugging and iterating on prompt graphs visually
Trade-offs: More of a development and testing tool than a production runtime. You'll need to export workflows to another system for production deployment. Smaller community than other visual builders.
Observability and Security Layers (Use Alongside Any Framework)
30. Guardrails AI
Input/output validation layer that sits on top of any LLM application. Define validators for content safety, PII detection, format compliance, and custom business rules. Works as middleware, not a replacement framework.
Security edge over LangChain: Adds a programmable safety layer between your application and LLM responses. PII detection, toxicity filtering, and custom validators run before outputs reach users.
Best for: Adding safety checks to existing LLM pipelines without rewriting
Trade-offs: Adds latency to every LLM call since responses must pass through validation. Doesn't replace your orchestration framework. Complex validator chains can become their own debugging challenge.
31. Langfuse
Open-source LLM observability platform. Self-hostable tracing, evaluation, and cost tracking. Integrates with LangChain, LlamaIndex, and custom LLM applications through a lightweight SDK.
Security edge over LangChain: Self-hosted deployment means your traces, prompts, and evaluation data never leave your infrastructure. Full audit trail for every LLM interaction.
Best for: Teams needing audit trails and cost tracking on their own servers
Trade-offs: Observability only. Doesn't execute or orchestrate anything. The self-hosted version requires PostgreSQL and infrastructure management. Some advanced features are only available in the cloud offering.
32. Braintrust
Prompt versioning, evaluation, and tracing platform with a focus on production LLM applications. Supports A/B testing of prompts and systematic evaluation of model outputs.
Security edge over LangChain: Centralized prompt management with version control and access controls. Evaluation data can be kept within your security boundary.
Best for: Teams with traceability requirements for production LLM apps
Trade-offs: The strongest features sit behind the paid tier. Free tier is useful for individual developers but limits team collaboration. Less established than Langfuse for self-hosted deployments.
33. Orq.ai
SOC2 certified LLM lifecycle management platform. GDPR and EU AI Act compliant. Offers prompt management, evaluation, and deployment tools with enterprise governance built in.
Security edge over LangChain: SOC2 certification and EU AI Act compliance from day one. Designed for organizations where regulatory compliance is a hard requirement, not an aspiration.
Best for: Enterprise teams needing compliant LLM lifecycle management
Trade-offs: Newer platform with less community content and fewer third-party tutorials. The compliance-first positioning means the developer experience can feel heavier than lighter-weight alternatives.
How to Choose the Right Secure LangChain Alternative
The right choice depends on your threat model and deployment constraints. A private AI platform approach works for organizations that need full control. Cloud-native options suit teams already invested in a specific provider. And lightweight libraries like DSPy or Instructor make sense when you want the smallest possible attack surface.
For teams evaluating chatbots vs AI agents, the framework choice shapes what's possible. Agent-heavy workloads need CrewAI or AutoGen. Document retrieval leans toward Haystack or LlamaIndex. Simple inference calls just need Ollama or LocalAI.
FAQ
1. Is LangChain safe for enterprise use?
LangChain can work in enterprise settings with significant security hardening. The default configuration routes data through external APIs, and the 400+ dependency tree increases attack surface. Most teams in regulated industries add self-hosted inference and custom security layers on top, or they move to a framework that handles these concerns natively.
2. What is the most secure LangChain alternative?
Depends on your threat model. For full data sovereignty with zero retention and cryptographic verification, Prem AI is purpose-built for that. For air-gapped environments, PrivateGPT or Ollama keep everything local. Cloud-native teams get strong isolation from Bedrock or Vertex AI within their respective ecosystems.
3. Can I use LangChain with self-hosted models?
Yes. LangChain supports Ollama, vLLM, and other local inference backends. But the framework still carries its full dependency surface, and many integrations default to cloud services. Switching to local inference doesn't eliminate the other security concerns.
4. What's the best open-source framework for building secure AI agents?
CrewAI and Haystack are strong options for self-hosted agent and RAG systems, though both come with their own learning curves. DSPy offers the smallest attack surface for programmatic LLM workflows. For small models in enterprise settings, pairing a lightweight framework with a self-hosted inference engine gives you the most control.
Conclusion
LangChain got a lot of teams from zero to prototype fast. That's real value. But prototyping and production are different problems, and the security gaps in LangChain's architecture become liabilities once you're handling real user data, regulated workloads, or proprietary IP.
The 33 alternatives on this list aren't all direct replacements. Some are full platforms. Some are single-purpose libraries. Some sit alongside whatever you're already running. The right pick comes down to three questions: where does your data need to stay, how much of the stack do you want to own, and what compliance requirements are non-negotiable?
If you're early in the decision, start with the comparison table above and narrow by use case. Teams that need data sovereignty from day one will save months by choosing a platform built for it rather than bolting security onto a framework that wasn't designed with it in mind.
The AI tooling landscape moves fast. New frameworks ship monthly. But the core principle stays the same: know where your data goes, control who touches it, and pick tools that make security the default rather than an afterthought.
If data sovereignty is non-negotiable for your team, start with Prem Studio or explore the docs.
