AI Avatars: 2025 Digital Content Transformation
AI avatars in 2025 transform digital content through real-time interactions, hyper-realistic animations, and multimodal AI integration. This technology powers virtual assistants, AI influencers, and accessibility tools, while also raising ethical and legal concerns across industries.

AI avatars are transforming digital content in 2025, enabling real-time interaction, hyper-realistic animation, and multimodal AI integration. These advancements power virtual assistants, AI-generated influencers, and accessibility tools, reshaping industries from media to customer service. However, their rise also introduces ethical and legal concerns, including bias, deepfake risks, and accountability. As AI avatars become more autonomous and integrate into the metaverse and enterprise applications, their impact on privacy, IP rights, and human-AI collaboration will shape the future of digital content.
The Rise of AI Avatars in Digital Content
In 2025, AI avatars have become a game-changer in digital content creation, offering hyper-realistic interactions powered by advancements in generative AI, multimodal learning, and real-time processing. From virtual influencers and AI-powered customer service agents to accessibility tools for deaf-hearing communication, these digital entities are reshaping how people interact with content.
The rapid evolution of transformer-based AI models, neural rendering, and speech synthesis has made it possible for AI avatars to mimic human-like expressions, gestures, and voice modulation with unprecedented accuracy. This shift is transforming industries such as media, gaming, e-commerce, and education, enabling brands and creators to automate and personalize digital experiences at scale.
However, as AI avatars gain autonomy and realism, they also raise ethical and legal concerns. Issues like bias in AI-generated personas, misinformation risks, and avatar accountability have sparked discussions on regulatory frameworks and responsible AI governance.
The Technological Backbone of AI Avatars
The rapid evolution of AI avatars in 2025 is powered by breakthroughs in generative AI, multimodal learning, and real-time processing. These advancements allow avatars to speak, gesture, and react dynamically, making them indistinguishable from human interactions in digital spaces. This section explores the core technologies behind AI avatars, from deep learning frameworks to real-time rendering techniques.
Generative AI and Neural Networks
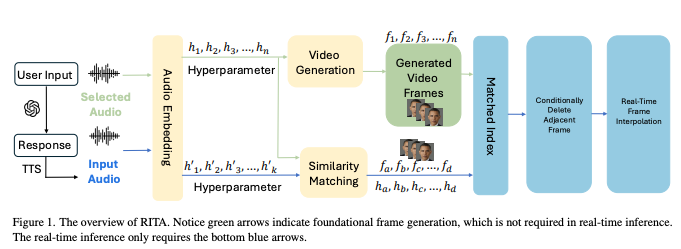
At the core of modern AI avatars lies transformer-based generative AI, enabling lifelike facial expressions, synchronized speech, and fluid movements. Large-scale neural networks trained on vast datasets generate highly realistic avatars capable of lip-syncing, emotional responses, and adaptive conversations.
Key advancements include:
- Text-to-Speech (TTS) & Speech-to-Text (STT): AI avatars now leverage real-time voice synthesis for natural speech generation.
- Face & Motion Synthesis: Models like RITA enable seamless lip-sync and expressive animations without pre-recorded datasets.
- Neural Rendering: AI-enhanced video synthesis techniques ensure high-fidelity visual quality with minimal computational load.
These technologies eliminate the need for pre-scripted animations, allowing avatars to respond naturally to user input, voice prompts, and contextual cues.
Multimodal AI: Speech, Vision, and Text Fusion
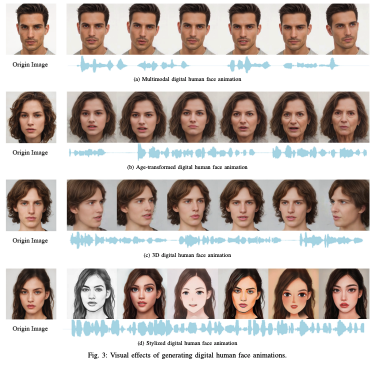
A critical factor in AI avatar realism is the fusion of multimodal data—combining speech, text, and vision to generate coherent, interactive digital personas.
- Large Language Models (LLMs) drive dialogue comprehension and response generation, ensuring context-aware, conversationally fluid avatars.
- Computer Vision & Gesture Recognition allow avatars to detect and replicate facial expressions and body language, enhancing realism.
- Audio-Visual Synchronization ensures avatars can speak, emote, and react in sync with textual inputs and emotional cues.
This integration bridges the gap between static digital avatars and truly interactive AI-driven personas, making them more engaging in fields like customer service, education, and entertainment.
Real-Time Processing and Optimization
For AI avatars to function seamlessly in live applications, latency reduction and performance optimization are essential. Recent innovations in real-time AI pipelines focus on:
- Low-Latency Inference Models: AI avatars now generate responses and animations within milliseconds, ensuring instantaneous interaction.
- Frame Interpolation for Smooth Animation: AI-driven video frame enhancement reduces motion artifacts, making avatars more lifelike and responsive.
- Scalable Cloud & Edge Computing: AI avatars are now deployed on lightweight edge devices, enabling real-time use in mobile applications and VR/AR environments.
These improvements mean that AI avatars can now operate in dynamic, real-world scenarios—responding instantly in live chats, virtual meetings, and interactive media experiences.
Real-World Applications of AI Avatars
AI avatars are reshaping industries by enhancing user interaction, automating content creation, and providing new levels of accessibility. From digital influencers and customer service agents to assistive technology for accessibility, these applications demonstrate the versatility of AI-driven avatars.
AI Avatars in Content Creation
The media and entertainment industry is rapidly adopting AI avatars to automate digital content production while maintaining high-quality, human-like engagement.
- AI-Powered Virtual Influencers: Digital personas like Lil Miquela have proven that AI-generated influencers can engage millions, collaborate with brands, and influence audiences without human intervention.
- Automated Video Production: AI avatars generate scripted or interactive video content, removing the need for actors, studios, and expensive production setups.
- AI-Driven Storytelling: Platforms integrate LLMs with avatars to create dynamic, branching narratives for gaming, interactive media, and personalized content experiences.
With AI, content personalization reaches new heights—tailoring avatars to specific audiences, languages, and cultural contexts with minimal manual input
AI Avatars for Accessibility and Inclusion
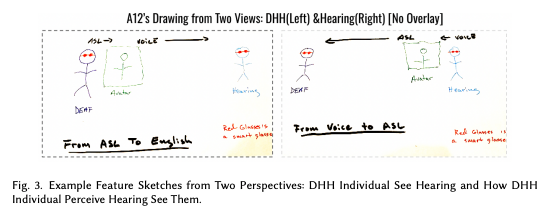
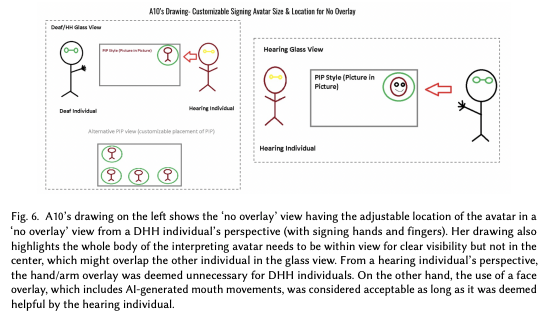
AI avatars are revolutionizing accessibility by enabling real-time multimodal communication. One of the most impactful use cases is AI-assisted sign language interpretation, bridging the gap between deaf and hearing individuals.
- Sign Language Avatars: AI avatars trained on gesture recognition models can interpret spoken words into sign language, making live events and digital content more inclusive.
- Speech-to-Sign AI: These avatars translate text or voice inputs into animated sign language gestures, supporting accessibility in education, healthcare, and customer service.
- Multilingual Avatars for Global Reach: AI avatars auto-translate conversations, allowing for seamless cross-language communication in real-time.
As virtual communication grows, these avatars help companies and public institutions provide equitable access to digital services.
AI Avatars in Customer Interaction and Virtual Assistants
AI avatars are revolutionizing customer engagement by offering lifelike, automated assistance across industries.
- AI-Powered Customer Support Agents: Companies now deploy avatars with LLM-based chatbots to provide personalized, 24/7 customer service.
- Virtual Assistants for Business & E-Commerce: AI avatars handle product inquiries, customer complaints, and onboarding processes with human-like interaction.
- Healthcare & Therapy Assistants: AI avatars assist in mental health counseling, patient monitoring, and wellness coaching, offering an interactive, empathetic digital experience.
With enhanced speech synthesis, facial expressions, and natural dialogue generation, AI avatars reduce operational costs while improving user experience and engagement.
Ethical and Legal Considerations in AI Avatar Deployment
AI avatars are stepping into human-like roles, but with this evolution comes a storm of ethical and legal dilemmas. What happens when an AI-generated persona is indistinguishable from a real person? Who takes the fall when an avatar spreads misinformation or reinforces biases? These are no longer sci-fi hypotheticals—they’re today’s pressing concerns.
The Hidden Bias in AI Avatars
For all their sophistication, AI avatars inherit the flaws of their training data. If an AI model is trained on imbalanced datasets, it can unintentionally favor certain demographics while underrepresenting others. The result? AI-generated personas that reflect racial, gender, and cultural biases, sometimes in ways that reinforce stereotypes instead of breaking them.
This bias isn’t just theoretical—it’s already surfaced. Studies have shown that AI-generated faces are often more accurate for lighter-skinned individuals, while voice synthesis models may struggle with accents and tonal variations. Imagine an AI avatar designed for global customer service but struggling to understand certain dialects. The experience suddenly feels less inclusive and more alienating than intended.
Then comes the misinformation problem. Deepfake technology has already demonstrated how AI-generated avatars can blur reality, making it difficult to distinguish between real and artificially constructed identities. In the wrong hands, this power could be weaponized for fraud, misinformation, or political manipulation.
So, where do we draw the line? And more importantly, who gets to decide?
The Legal Maze of AI Avatars
Laws weren’t built for synthetic humans, which makes AI avatar regulation a legal gray area. If an AI avatar is used to impersonate someone, does it fall under identity theft laws? If a company uses an avatar to replace human actors, does it owe royalties to the original creators? And what happens when an AI-generated customer service agent misguides a user with false information—who’s legally responsible?
Here are some of the key concerns keeping legal experts up at night:
- Intellectual Property & Ownership
- If an AI avatar mimics a real person’s likeness, who owns the rights? The individual? The company that trained the model? No one? These questions are at the heart of emerging lawsuits.
- Privacy & Data Protection
- AI avatars require vast amounts of voice, facial, and behavioral data. But where does this data go? Is it stored securely, or does it end up fueling future AI training without consent?
- Accountability in AI-Generated Decisions
- AI avatars are being deployed in customer service, healthcare, and even legal assistance, but who takes the blame if they provide incorrect or misleading information? A flawed AI-generated diagnosis or legal recommendation could have real-world consequences.
Governments and industry leaders are scrambling to create regulations, but the pace of AI development is faster than the legal system can adapt. Some countries are pushing for AI transparency laws, requiring companies to disclose when users are interacting with an AI avatar instead of a human. Others are debating whether AI avatars should be granted some form of “legal personhood”, similar to corporations, to hold them accountable for their actions.
For now, the rules remain blurry. But as AI avatars continue to blend into our digital lives, expect new policies, lawsuits, and ethical debates to reshape how we interact with virtual humans.
Bringing It All Together
AI avatars aren’t just a technological breakthrough—they’re a societal shift. They can enhance accessibility, automate workflows, and create entirely new forms of digital interaction, but they also challenge our definitions of trust, identity, and accountability. The technology is here. The question is: are we ready for it?
AI Avatars and the Future of Digital Content
If the last decade was about making AI functional, 2025 is about making AI feel human. AI avatars are no longer just tools—they are interactive, expressive, and capable of driving engagement in ways never seen before. But as they seep into the fabric of digital content, the real question isn’t just what they can do, but where they will take us next.
The Integration of AI Avatars into the Metaverse and Virtual Worlds
The metaverse is no longer just a buzzword—it’s becoming a living, evolving digital ecosystem where AI avatars are set to play a starring role.
- Virtual Assistants in Immersive Environments
- AI avatars are stepping beyond customer service and into real-time, persistent virtual guides, shaping user experiences in digital stores, virtual workplaces, and interactive learning spaces.
- In metaverse platforms, they can adapt in real-time, responding to voice commands, contextual inputs, and even emotional cues.
- AI-Powered Digital Twins
- The concept of personalized AI avatars is gaining traction. Imagine a digital version of yourself that remembers your preferences, interacts with others on your behalf, and even negotiates deals in virtual spaces.
- Synthetic Media & Virtual Production
- AI avatars will reshape content creation by automating digital performances, reducing production costs, and creating hyper-personalized media experiences.
- Some studios are already using AI-driven avatars to recreate historical figures, generate fictional characters, or even replace traditional actors in commercial settings.
It’s clear that AI avatars aren’t just inhabiting the metaverse—they are helping build it.
Hyper-Personalization: AI Avatars in Everyday Digital Interactions
Beyond grand virtual worlds, AI avatars are becoming an everyday presence in our digital lives. They’re customized to individual users, adapting to emotions, behaviors, and preferences.
- AI-Powered Personal Trainers & Life Coaches
- Imagine an AI avatar that remembers your fitness goals, tracks your progress, and gives you real-time motivation based on your mood and habits.
- In mental health, AI avatars act as digital therapists, offering non-judgmental support, guided meditations, and cognitive behavioral therapy exercises.
- Next-Gen AI Chat Companions
- Virtual companions are evolving beyond chatbots and voice assistants into fully animated, emotionally aware AI friends, capable of sustained, evolving conversations.
- AI Avatars in Workplace Automation
- Businesses are deploying AI avatars to handle corporate training, customer interactions, and even internal team collaboration, reducing workload while maintaining high engagement.
With multimodal learning and real-time adaptation, AI avatars will no longer feel like scripted AI assistants—they will feel like real entities woven into our lives.
The Road Ahead: Challenges & Opportunities
The future of AI avatars is brimming with potential, but it comes with its share of obstacles.
- Ethical AI Governance:
- As AI avatars become more lifelike, ensuring transparency and preventing deceptive use will be a top priority.
- Some countries are exploring legislation that requires companies to disclose when users are interacting with AI.
- Balancing Automation & Human Creativity:
- AI avatars can enhance digital experiences, but should they completely replace human creators, actors, or influencers?
- Many industries are walking a fine line between automation and preserving human artistic value.
- Scaling AI Avatars for Mass Adoption:
- The next big leap will be making AI avatars more affordable, accessible, and seamlessly integrated into existing platforms.
Despite these challenges, one thing is certain: AI avatars are not just a passing trend. They are the foundation of the next era of digital content—one where interactions feel organic, experiences are deeply personalized, and the boundaries between real and artificial become increasingly blurred.
Are we ready? Whether we are or not, the future of AI-driven digital content is already here.
References:



















