15 Best Lightweight Language Models Worth Running in 2026
Compare 15 lightweight language models by parameters, performance, and use case. From Qwen3 to Gemma 3n, find the right small LLM for coding, chatbots, or on-device AI.

Most teams don't need a 70B parameter model. They need something that fits on a single GPU, responds in milliseconds, and handles the actual workload without burning through cloud credits.
Lightweight language models fill that gap. Roughly under 10B parameters, built for lower compute, faster inference, and real deployment on edge devices, laptops, and modest server hardware.
Below are 15 worth knowing in 2026, compared by size, strengths, hardware needs, and where they actually fit.
What Counts as a Lightweight LLM?
Typically 0.5B to 10B parameters. Models that run on consumer hardware or a single data center GPU without needing a multi-node cluster.
What changed in 2026 is how capable these small models got. Quantization formats like GGUF cut memory requirements in half without wrecking quality. Knowledge distillation transfers reasoning from large models into tiny packages. And demand is real: on-device AI, privacy-first deployments, and inference cost pressure all push teams toward smaller models.
The trade-off still exists. A 3B model won't match GPT-4 on open-ended creative writing. But for classification, extraction, translation, or domain-specific Q&A, the gap is narrower than most people assume. Especially after fine-tuning on your own data.
All 15 Models at a Glance
The 15 Best Lightweight Language Models
1. Qwen3-8B
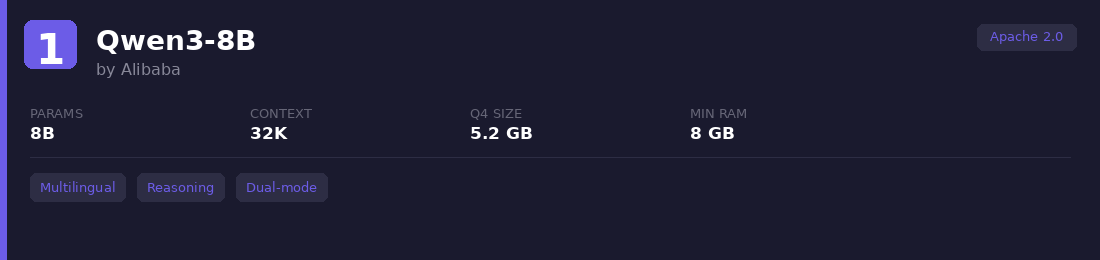
Alibaba's 8B model supports 119 languages and toggles between a "thinking" mode (step-by-step reasoning) and a fast direct-answer mode. Competes with models 4x its size on math and coding. Available on Ollama as qwen3:8b.
Best for: Teams that need multilingual coverage and solid reasoning in one package.
Watch out: Thinking mode roughly doubles token usage. It also struggles with spatial reasoning tasks like 3D simulations and can be over-cautious on politically sensitive topics.
2. Gemma 3n E2B
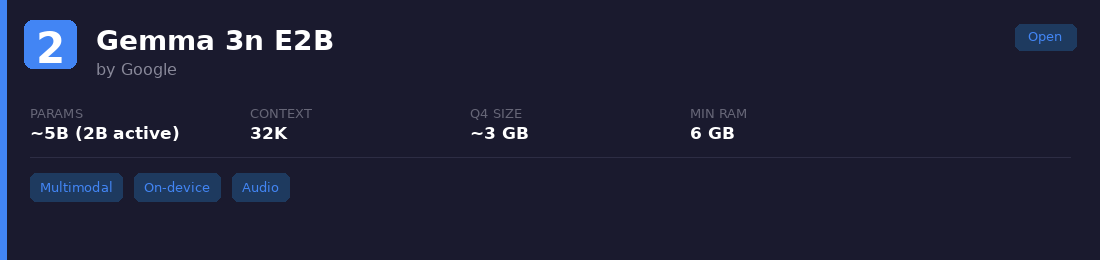
Google built this for phones and laptops. 5B total parameters but only 2B active at inference through per-layer embedding, keeping memory low. Handles text, images, audio, and short video clips natively.
Best for: On-device multimodal apps where you need text + vision + audio in one model.
Watch out: Context capped at 32K (Gemma 3 gets 128K). Audio limited to 30-second clips. Without PLE caching on fast storage, memory use nearly triples. Quantization cuts math accuracy by about 5%.
3. Llama 3.1 8B Instruct
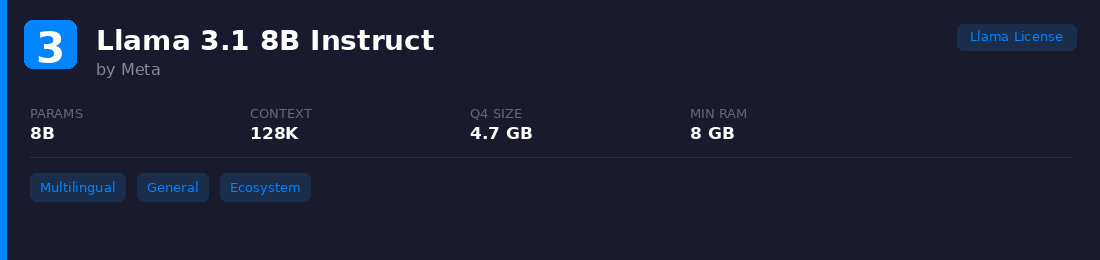
Meta's workhorse 8B model, trained on 15T+ tokens. Strong across English and seven other languages. Massive community support means you'll find it quantized, fine-tuned, and integrated into basically every tool.
Best for: General-purpose chat, multilingual tasks, and anything where broad ecosystem compatibility matters.
Watch out: The Llama license restricts usage for apps with 700M+ monthly active users. Performance degrades noticeably beyond 64K context in practice, even though it technically supports 128K.
4. Phi-4 Mini
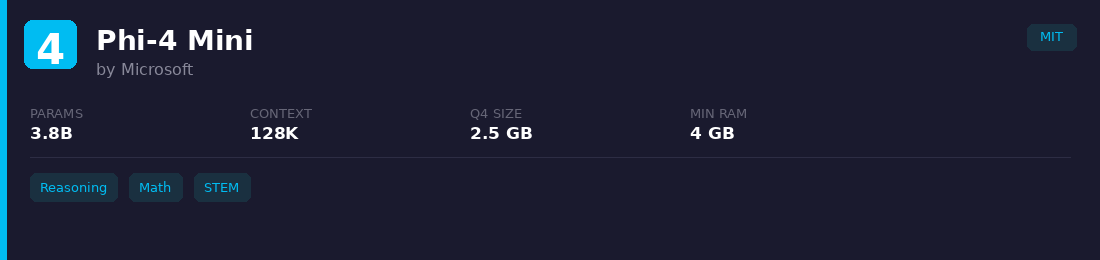
Microsoft's 3.8B model punches hard on reasoning and math. Trained on synthetic data and textbooks, giving it unusually strong analytical ability for its size. Runs on edge devices with 4 GB RAM when quantized.
Best for: STEM tasks, structured reasoning, and use cases where you need analytical depth from a tiny footprint.
Watch out: Factual knowledge is thin at 3.8B parameters. Multilingual support is limited since training skewed heavily toward English. Code generation works for Python but drops off for less common languages.
5. Mistral 7B
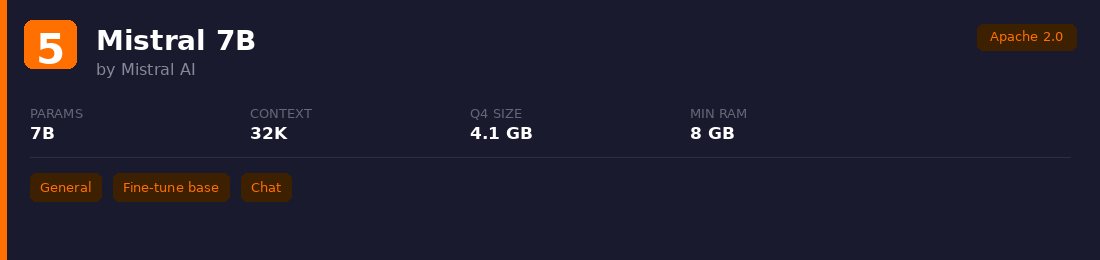
The model that proved 7B could compete with much larger alternatives. Uses grouped-query attention and sliding window attention for efficient inference. Still one of the most popular base models for self-hosted deployments.
Best for: General chat, translation, and as a solid fine-tuning base when you want a permissive license.
Watch out: Users report formulaic, verbose output compared to newer alternatives like Qwen3. It also lacks built-in content moderation, which caused some early controversy around safety. Showing its age against 2026 competitors.
6. SmolLM3-3B
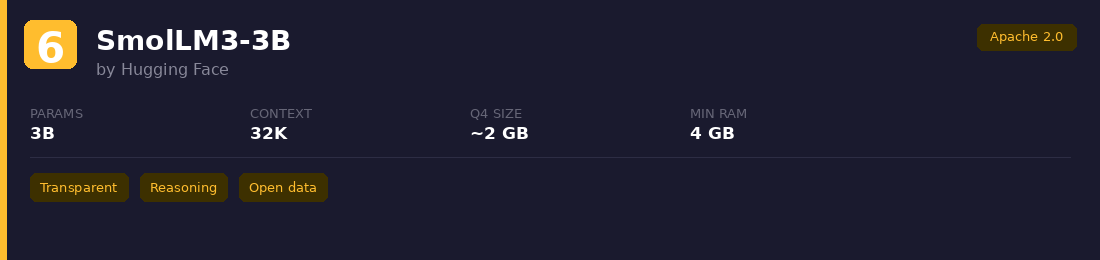
Hugging Face's fully transparent 3B model, trained on 11T tokens with the entire training pipeline open-sourced. Benchmarks put it ahead of Qwen3-4B and Gemma 3 4B on several reasoning tasks.
Best for: Teams that want full visibility into training data and methodology, or need a strong sub-4B reasoning model.
Watch out: Still new. Community fine-tunes and tooling are thinner than Llama or Qwen. Generated content needs proper evaluation since factual accuracy can be inconsistent at this size.
7. Qwen3-4B
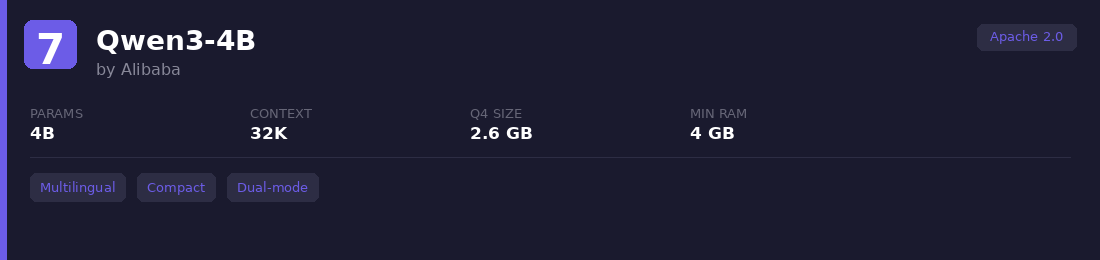
The 4B variant in Alibaba's Qwen3 family. Same dual-mode (thinking/non-thinking) architecture as the 8B version, just more compact. Supports the same 119 languages and uses GQA for efficient inference. Alibaba claims it rivals Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct on some benchmarks.
Best for: When 8B is too heavy for your hardware but you still want multilingual reasoning capability. Works well with LoRA-based fine-tuning on narrow tasks.
Watch out: Noticeable quality drop on complex coding and multi-step reasoning compared to the 8B sibling. The thinking mode's token overhead hits harder at this size since you're already working with limited capacity.
8. DeepSeek-R1 Distill (1.5B / 8B)
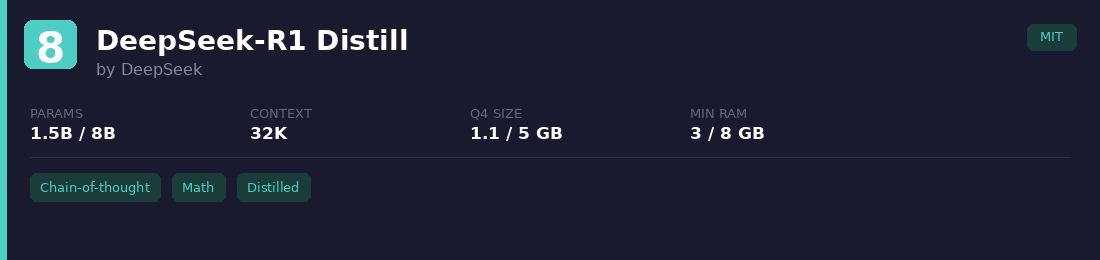
DeepSeek took their R1 reasoning model and distilled it into smaller variants based on Qwen and Llama architectures. The 1.5B version is the smallest model with genuine chain-of-thought reasoning. The 8B version outperforms some models at the 30B+ range on math benchmarks.
Best for: Math, logic, and structured problem-solving where you need step-by-step reasoning on limited hardware.
Watch out: Distillation weakens safety guardrails. Independent testing shows high vulnerability to adversarial prompts. Repetitive outputs if temperature isn't set between 0.5 and 0.7, and occasional language mixing in responses.
9. Gemma 3 4B
Google's 4B model with native vision. Processes images alongside text in a single pass, supports 128K context, and covers 35+ languages. ShieldGemma safety classifier built in.
Best for: Vision-language tasks at a compact size. Document understanding, image captioning, visual Q&A.
Watch out: Vision adds memory overhead on top of the 4B text model. Image resolution is fixed between 256 and 768 pixels. Text-only performance lags behind Qwen3-4B and SmolLM3 on several reasoning benchmarks.
10. GLM-4-9B-0414
Zhipu AI's 9B model, trained with reinforcement learning on code, function calling, and web design. Generates clean SVG graphics and HTML artifacts. Supports tool use natively with JSON-based function calling.
Best for: Code generation, artifact creation, and agent workflows that need function calling baked in.
Watch out: Has not received the same agent capability enhancements as the larger 32B version. Optimized mainly for batch operations like translation rather than complex multi-step agent tasks. Needs YaRN for inputs beyond 32K tokens.
11. Qwen3-0.6B

At 600M parameters, one of the smallest models with basic reasoning and multilingual text. Same thinking/non-thinking toggle as its larger siblings. Built for edge deployment and lightweight agent workflows.
Best for: Ultra-constrained environments: IoT devices, mobile apps, browser-based inference.
Watch out: Anything beyond simple classification, extraction, or short Q&A will push past its limits. Useful as a routing model or first-pass filter, not a standalone assistant.
12. TinyLlama 1.1B

A community-trained 1.1B model built on the Llama 2 architecture, trained on 3T tokens. Runs on CPU with just 2-4 GB RAM when quantized. The entire training codebase is open. Proof that you don't need enterprise hardware to run useful inference.
Best for: Minimal hardware environments: Raspberry Pi, old laptops, basic text extraction pipelines where latency matters more than quality.
Watch out: Quality ceiling is low. The 2K context window is tiny by 2025 standards. Fine-tuning on a narrow task is almost mandatory to get useful results.
13. Phi-4 Mini Reasoning
Microsoft took Phi-4 Mini and added reinforcement learning for math and science reasoning. Same 3.8B footprint, with chain-of-thought traces baked in. Higher scores than base Phi-4 Mini on STEM benchmarks. A good example of how custom reasoning models outperform generic ones on specific tasks.
Best for: Math tutoring, scientific computation, and logic-heavy workflows where you want explicit reasoning steps.
Watch out: Reasoning traces increase token usage. Inherits Phi-4 Mini's knowledge gaps and English-centric training. Outside STEM, the base version is faster.
14. StableLM Zephyr 3B
Stability AI's 3B instruction-tuned model with DPO alignment from UltraFeedback. Outperformed Llama 2 70B on MT-Bench at launch, notable for a model 23x smaller.
Best for: Basic instruction following, Q&A, and text extraction on constrained hardware.
Watch out: Released late 2023, so it's behind newer 3B models like SmolLM3 on most benchmarks now. The 4K context is limiting. StabilityAI license restricts commercial use.
15. Qwen3-1.7B
Sits between the 0.6B and 4B Qwen3 variants. Same architecture, same dual-mode reasoning, same 119 language support. A meaningful step up from 0.6B without the memory cost of 4B.
Best for: Edge deployment where 0.6B isn't enough and 4B is too heavy. Lightweight agents, classification, multilingual routing.
Watch out: Limited on complex generation. Works best for short, structured outputs. For nuanced conversation, step up to 4B or 8B.
How to Pick the Right Lightweight LLM
Start with the task, not the model.
Need coding + reasoning? Phi-4 Mini or GLM-4-9B.
Need multilingual at scale? Qwen3-8B or Llama 3.1 8B.
Running on a phone or IoT? Gemma 3n or Qwen3-0.6B.
Need multimodal (text + image + audio)? Gemma 3n is the only sub-10B option covering all three.
Want to fine-tune on your own data? Pick any Apache 2.0 model. A fine-tuned 3B model often outperforms a general 70B model on your specific task at a fraction of the cost.
If you're heading the fine-tuning route, end-to-end pipelines that handle dataset prep, training, and evaluation in one flow save weeks of setup.
FAQ
1. What's the smallest LLM that's actually useful?
Qwen3-0.6B handles basic tasks, agent workflows, and multilingual text reasonably well. For anything beyond simple extraction or classification, 1.5B to 3B is a safer floor.
2. Can lightweight LLMs run on a laptop without a GPU?
Yes. Models under 3B run on CPU with 8-16 GB RAM when quantized to Q4. TinyLlama and Qwen3-0.6B are the most laptop-friendly. Slower than GPU, but perfectly usable for interactive tasks.
3. How do lightweight LLMs compare to GPT-4 for enterprise tasks?
They won't match GPT-4 on open-ended reasoning or creative generation. But for focused tasks like classification, extraction, and domain-specific Q&A, a fine-tuned lightweight model often matches or beats it at a fraction of the cost. The key is cutting API costs by running smaller models on your own infrastructure.
4. Is it better to fine-tune a small model or run a bigger one out of the box?
For specific tasks, fine-tuning almost always wins. A 3B model trained on your data can outperform a general 70B model on your exact use case, with 10x lower inference costs.
If you're evaluating lightweight models for production, the next step is fine-tuning on your own data. Prem Studio handles dataset prep, training, and evaluation in one place, and supports 30+ base models including most of the ones listed above.
