Chatbots vs AI Agents – Which is Right for Your Business?
Customer support has evolved from simple chatbots to AI agents that manage context, automate tasks, and assist in real time. This blog compares chatbots, LLM chatbots, and AI agents to help businesses choose the right solution for smarter, scalable support with PremAI

AI in Customer Support: From Basic Automation to Intelligent Agents
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in customer support has significantly evolved, transforming basic customer interactions into sophisticated, context-aware dialogues. Understanding the distinctions between traditional chatbots and intelligent AI agents is critical for businesses looking to enhance customer experiences and streamline operational efficiencies.
Traditional Chatbots: Rule-based and NLP
Chatbots emerged as a frontline solution to customer inquiries, initially employing simple, rule-based structures. These early chatbots utilized predefined scripts to provide standard responses to common customer questions. With NLP, chatbots changed from simple rule-based tools into smarter systems that understand context and hold better conversations.
NLP-enhanced chatbots use advanced language understanding algorithms to interpret user queries more flexibly and accurately. Techniques such as intent recognition, entity extraction, and sentiment analysis help these bots to understand context better and respond appropriately to customer interactions. For example, an NLP chatbot can understand what a customer wants, give the right answer, or pass tough questions to a human.
Yet, despite these advancements, traditional chatbots have distinct limitations. They mostly work only for fixed questions and answers, and have trouble remembering context, handling long chats, or keeping up with changing conversations. Consequently, these chatbots are typically suited to handling simple, repetitive customer support tasks.
Common Deployment Scenarios for Traditional Chatbots Include:
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) automation
- Appointment scheduling and cancellations
- Simple transactional interactions (e.g., checking account balances)
LLM-Based Chatbots: The Middle Ground Between Traditional Chatbots and AI Agents
Large Language Model (LLM)-based chatbots, such as ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini, represent an evolution beyond traditional rule-based bots. These systems leverage transformer-based architectures and vast pre-trained knowledge to deliver fluid, natural, and more context-aware conversations.
Unlike traditional chatbots, LLM-powered chatbots can:
- Generate human-like responses by understanding and predicting natural language patterns.
- Handle multi-turn conversations, maintaining better context awareness over time.
- Answer a wider range of queries beyond pre-defined intents, making them more flexible.
However, while LLMs have improved context retention and conversational flexibility, they lack structured workflow automation and decision-making capabilities. Unlike AI agents, they cannot autonomously execute tasks, interact with APIs, or trigger business processes. This means that while LLMs improve customer interactions, they still require external integrations to handle complex workflows.
Common Deployment Scenarios for LLM-Based Chatbots Include:
- Customer Query Handling: Answering open-ended customer inquiries with more natural, detailed responses.
- Content Generation & Summarization: Assisting users by reformatting or summarizing complex information.
- Internal Knowledge Assistants: Acting as enterprise knowledge bases to assist employees in retrieving information.
Advanced AI Agents: Contextual Understanding and Workflow Automation
In contrast, advanced AI agents represent the next generation of AI-powered customer support. These intelligent systems go beyond traditional chatbot capabilities, embedding deeper contextual understanding, more sophisticated dialogue management, and robust workflow automation capabilities.
Advanced AI agents integrate AI techniques such as deep learning, transformer-based models, and real-time adaptive systems to manage nuanced, context-sensitive customer interactions. These agents not only interpret the customer's immediate query but also analyze the historical context, user profiles, and situational factors to deliver highly personalized and efficient responses.
Furthermore, AI agents can proactively initiate interactions, anticipate customer needs, and automate complex workflows through actionable dialogues. They typically integrate into enterprise systems and databases, enabling them to execute more intricate tasks seamlessly, such as modifying customer records, initiating transactions, or providing technical troubleshooting.
Key features differentiating AI agents from chatbots include:
- Conversational Memory: The ability to retain and leverage historical conversation context to deliver relevant, accurate responses.
- Dynamic Workflow Automation: Capability to autonomously execute business processes based on conversational inputs, significantly reducing human intervention.
- Proactivity and Adaptability: The capability to proactively engage users based on inferred needs or previous interactions, as well as to adapt in real-time to user feedback and conversational dynamics.
AI agents thus provide significant advantages in situations requiring deeper personalization, multi-step processes, and intricate customer interactions. These advantages often result in increased customer satisfaction, reduced operational costs, and improved business efficiency.
Typical Deployment Use Cases for Advanced AI Agents Include:
- Complex issue resolution in tech support scenarios
- Personalization-intensive interactions, such as finance or healthcare customer service
- Automation of dynamic business processes involving multiple user inputs and interactions
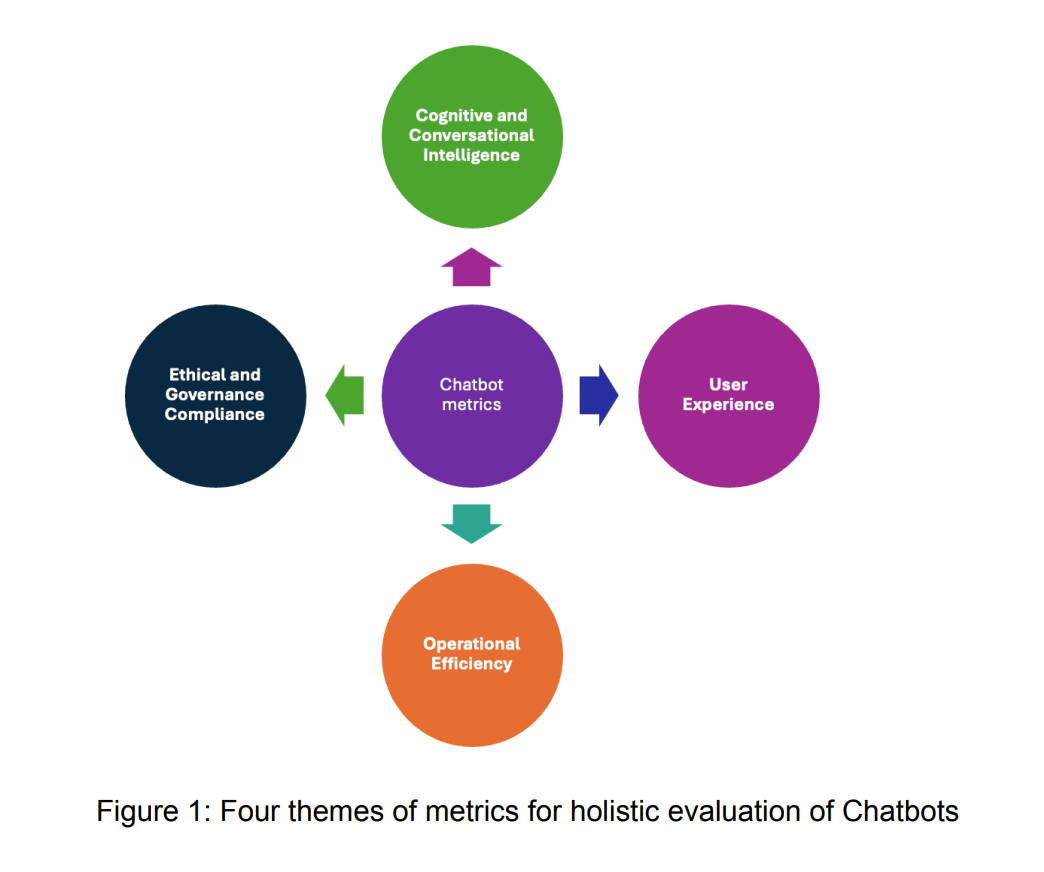
Evaluating Performance: Chatbots vs AI Agents
To effectively choose between traditional chatbots and advanced AI agents for customer support, businesses need to accurately evaluate performance using clearly defined frameworks and metrics. This section explores essential technical criteria, evaluation frameworks, and real-time conversational capabilities to help businesses determine the most suitable AI solution.
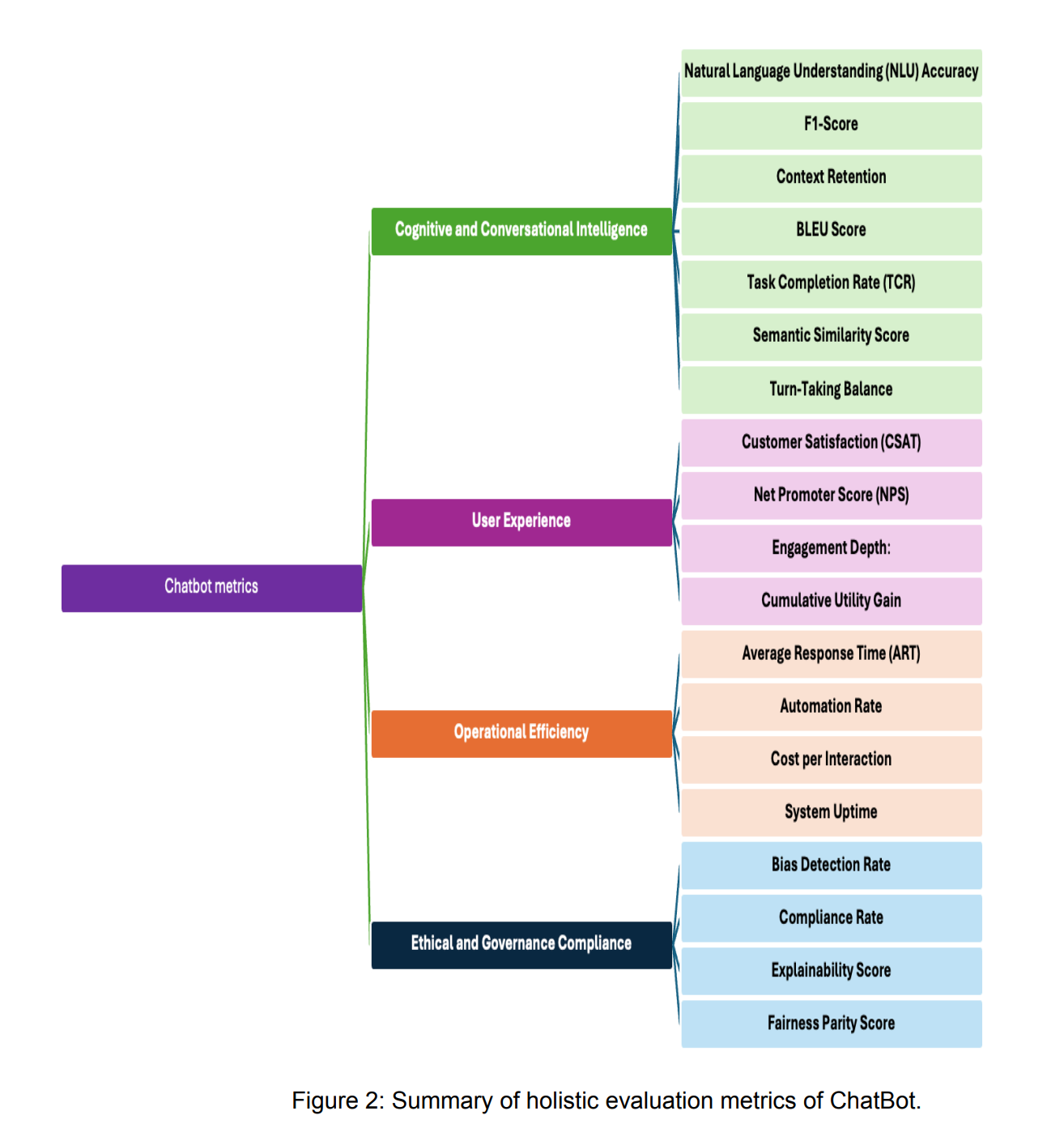
Evaluation Frameworks and Metrics for AI-Powered Customer Support
Evaluating conversational AI technologies requires comprehensive metrics and frameworks capable of capturing a wide range of performance aspects, from language understanding to customer satisfaction. Here are key criteria essential for thorough evaluation:
Essential Evaluation Metrics:
- Accuracy & Precision: Determines the chatbot or agent's ability to provide correct responses. Metrics include intent detection accuracy, entity extraction accuracy, and response correctness.
- Context Retention: Measures the AI's capability to retain and utilize conversational history to enhance interaction quality, evaluated using metrics such as Contextual Accuracy and Memory Retention Rate.
- Response Speed & Scalability: Evaluates the AI’s response time and its ability to scale seamlessly to handle increased customer interactions. Metrics here include Average Response Time (ART) and Throughput.
- User Satisfaction Metrics: Gauges customer satisfaction with the conversation experience, often captured through direct user feedback (CSAT scores, NPS scores).
Frameworks for Comprehensive Evaluation:
A robust evaluation framework outlined in recent research emphasizes multiple dimensions, including user satisfaction, task completion rate, and conversational quality. Such frameworks integrate automated evaluation methods and human judgment, enabling holistic performance analysis and actionable insights to improve conversational AI effectiveness.
Real-Time Conversation Handling: Chatbots versus AI Agents
Real-time responsiveness is crucial for customer satisfaction in conversational support scenarios. The technical architecture and underlying algorithms greatly influence how efficiently conversational systems handle real-time interactions.
Real-Time Challenges for Traditional Chatbots:
Traditional chatbots generally operate using predefined conversational flows and NLP techniques limited to simple intent recognition. As conversations become more complex, real-time performance can degrade, resulting in delayed or incorrect responses, reducing overall customer satisfaction.
Specific challenges include:
- Difficulty managing unexpected user inputs or off-script interactions.
- Limited adaptability in handling context shifts during real-time exchanges.
- Rigid workflows that struggle with dynamic conversation changes.
Advanced Real-Time Performance of AI Agents:
Advanced AI agents significantly outperform traditional chatbots in real-time scenarios due to their sophisticated algorithms, such as transformer-based models, and adaptive workflow capabilities. Key advantages include:
- Dynamic Intent Detection: AI agents dynamically detect evolving user intents in real-time, maintaining high response accuracy and appropriateness.
- Contextual Flexibility: Agents effectively retain and utilize conversation context, swiftly adapting responses in dynamic real-time interactions.
- Workflow Responsiveness: The ability to automatically trigger workflows based on real-time user inputs ensures seamless handling of complex requests without noticeable delays.
Recent research ("Beyond-RAG", link below) emphasizes that advanced AI systems equipped with Question Identification and Real-Time Answer Generation capabilities greatly enhance customer experience by rapidly processing and generating accurate, contextually relevant responses on the fly. This responsiveness drastically improves user satisfaction metrics compared to traditional NLP-based chatbots.
LLM-Based Chatbots: Enhanced Real-Time Conversations but Limited Task Execution
Large Language Model (LLM)-powered chatbots, such as ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini, introduce a significant improvement over traditional rule-based chatbots in real-time interactions. By leveraging transformer-based architectures, these chatbots can handle fluid, multi-turn conversations with greater context retention.
How LLM-Based Chatbots Improve Real-Time Conversations:
- Better Context Awareness: Unlike rule-based chatbots, LLMs dynamically retain conversational memory, allowing for cohesive, multi-turn interactions.
- More Human-Like Responses: LLMs generate natural, diverse responses, improving the quality of customer engagement.
- Handling Open-Ended Queries: These chatbots can generalize responses beyond predefined scripts, making them more adaptable to unexpected user inputs.
However, LLM-based chatbots still lack structured workflow execution capabilities. While they can handle complex conversations, they struggle with real-time task automation, such as triggering backend processes, integrating with APIs, or making structured business decisions.
Thus, while LLMs significantly enhance conversational experiences, they still require external integrations or hybrid AI models to match the full automation capabilities of AI agents.
Technical Implementation: Developing Robust AI-Powered Solutions
Implementing AI-driven customer support solutions requires a robust technical foundation. While traditional chatbots rely on simpler architectures, advanced AI agents demand sophisticated infrastructure, leveraging large-scale machine learning models and workflow automation. This section explores the core technical components essential for deploying and scaling AI-powered customer support systems.
Infrastructure Requirements and Scalability
The underlying infrastructure determines the scalability, efficiency, and real-time responsiveness of an AI-powered customer support system. Chatbots and AI agents differ significantly in their deployment architectures.
Chatbot Infrastructure: Rule-Based and NLP Models
Traditional chatbots are typically lightweight, requiring minimal computational resources. Their architecture consists of:
- Intent Recognition Systems: NLP-based frameworks, such as spaCy, NLTK, or Rasa, that identify user intent from predefined intents and entities.
- Predefined Flow Engines: Rule-based dialog flow engines like Dialogflow or IBM Watson Assistant, which operate based on structured response trees.
- Basic Cloud or On-Premise Deployment: Low computational needs allow chatbots to be hosted on cloud-based services such as AWS Lambda or Firebase Functions.
However, these chatbots struggle with scalability in complex conversational environments due to their static, rule-based nature.
LLM-based Chatbots Infrastructure: Transformer-Based Architectures and Integration Needs
Large Language Model (LLM)-based chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini present more sophisticated infrastructure needs compared to traditional chatbots. They rely on advanced transformer-based models and more powerful computational resources, typically requiring:
- Transformer-based Language Models: Utilize transformer architectures, enabling better context retention, language generation, and more nuanced conversations.
- GPU-accelerated Cloud Infrastructure: Often deployed using platforms such as AWS SageMaker, Azure OpenAI Service, or Google Cloud Vertex AI to efficiently handle computationally intensive inference workloads.
- Integration Middleware: LLM-chatbots generally lack built-in execution capabilities, necessitating integration middleware to communicate with external APIs and backend systems.
Despite offering greater conversational quality and flexibility, LLM-based chatbots generally do not include robust, native task automation capabilities found in full-fledged AI agents, thus requiring additional tooling and integrations to achieve comprehensive workflow automation.
AI Agent Infrastructure: Transformer Models and Adaptive Learning
AI agents operate on a far more complex infrastructure designed to handle contextual understanding and real-time dynamic responses. Their architecture includes:
- Transformer-Based NLP Models: Advanced LLMs such as GPT-4, Claude, and ProxyLLM facilitate text comprehension, intent detection, and conversation memory retention.
- Vector Databases for Context Storage: Unlike traditional chatbots, AI agents rely on vector databases (e.g., FAISS, Pinecone, Weaviate) to maintain conversational context and user history.
- Scalable Cloud Infrastructure: AI agents require distributed cloud architectures, including Kubernetes-based microservices or specialized GPU-accelerated models deployed on AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
This infrastructure allows AI agents to scale dynamically, handling high volumes of customer interactions without compromising performance.
Leveraging LLMs for Text-Style Transfer and Conversational Accuracy
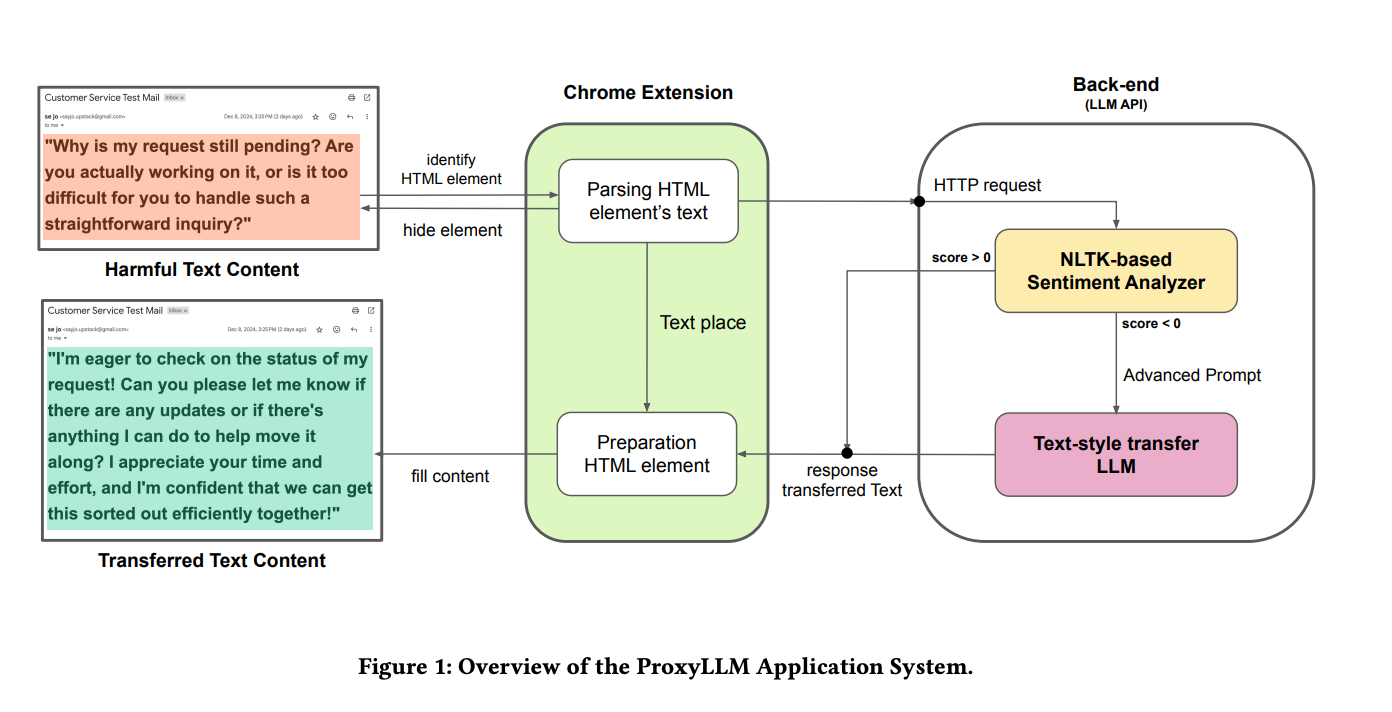
One of the key differentiators of AI agents is their ability to adjust responses dynamically based on customer sentiment, tone, and engagement style. This capability is made possible by text-style transfer—a method that modifies responses based on customer preference while maintaining accuracy.
Text-Style Transfer in AI Agents
Text-style transfer enables AI agents to adapt to different communication styles, improving engagement quality. Key techniques include:
- Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF): AI models fine-tune responses based on historical user interactions and explicit feedback.
- Sentiment Analysis for Contextual Adaptation: AI agents dynamically adjust their tone (formal, casual, empathetic) based on detected sentiment.
- Transformer-Based Style Adjustments: Using ProxyLLM, AI agents modify their response patterns while retaining semantic integrity.
This flexibility contrasts with traditional chatbots, which generate static responses that often lack personalization.
Impact of Text-Style Transfer on Customer Experience
- Higher User Engagement: Personalized responses increase interaction satisfaction.
- Reduced Escalations to Human Agents: More accurate and empathetic AI responses decrease the need for manual intervention.
- Improved Trust and Brand Alignment: AI agents that match a company’s brand tone enhance credibility and customer trust.
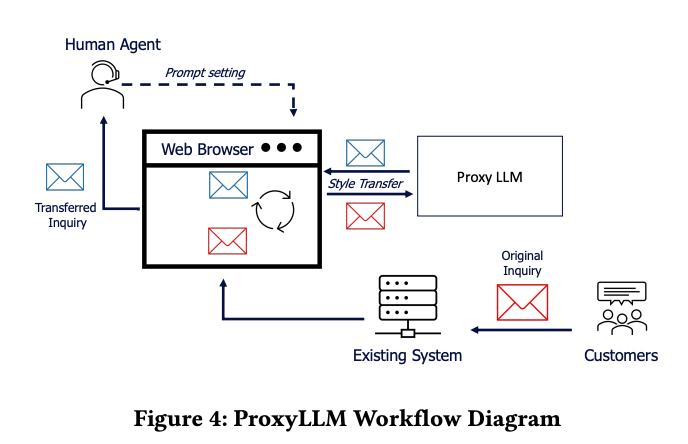
Workflow Automation: Bridging AI Agents with Business Processes
One of the most significant advancements in AI-driven customer support is workflow automation. AI agents extend beyond simple query resolution by triggering automated workflows that streamline business operations.
Automated Workflows in AI Agents
AI agents leverage conversational data to execute real-world actions. This is achieved through:
- Event-Triggered Responses: AI agents analyze customer intent and initiate automated workflows based on predefined conditions.
- API-Driven Business Process Integration: Connecting AI agents to enterprise APIs (CRM, ticketing systems, payment gateways) enables real-time task execution.
- Decision Trees with Machine Learning: Instead of rigid rule-based logic, AI agents use dynamic decision trees, adjusting actions based on evolving conversational data.
For example, a customer complaint workflow in an AI-driven system would:
- Identify a customer’s frustration via sentiment analysis.
- Retrieve previous interaction data from a vector database.
- Trigger a service ticket or escalate to a specialized human agent.
This workflow-based approach significantly reduces manual intervention and enhances operational efficiency.
Comparison: Chatbots vs AI Agents in Workflow Automation
AI agents surpass traditional chatbots by functioning as operational enablers rather than just conversational responders.
From Conversations to Automated Workflows
AI-powered customer support has evolved beyond simple question-answering to become a critical component of business process automation. AI agents, unlike traditional chatbots, do not just respond to queries, they dynamically trigger workflows, execute tasks, and integrate with enterprise systems.
This section explains how AI-driven workflow automation enhances efficiency and how conversational AI transitions from passive interaction to real-time task execution.
Understanding Workflow Automation in AI Agents
AI agents are designed to process unstructured conversations and extract actionable workflows. This process involves:
- Intent Detection – Identifying user intent beyond simple FAQ responses.
- Context Retention – Remembering previous interactions to generate accurate actions.
- Dynamic Decision-Making – Using AI models to determine the next best action based on conversational context.
For example, an AI agent in a banking support system can:
- Identify that a customer wants to dispute a transaction.
- Retrieve the transaction details from the CRM.
- Trigger a workflow to escalate the dispute to the fraud department.
This advanced approach removes manual intervention, accelerating customer issue resolution.
Comparison: Chatbots vs AI Agents in Workflow Automation
| Feature | Traditional Chatbots | AI Agents |
|---|---|---|
| Workflow Execution | Basic pre-programmed flows | Dynamic API-driven workflows |
| Context Awareness | Limited to predefined scripts | Retains and processes conversation history |
| Proactivity | Passive response-based interactions | Initiates actions based on inferred needs |
| Scalability | Struggles with complex interactions | Handles multi-step, real-time processes |
| Feature | Traditional Chatbots | AI Agents |
|---|---|---|
| Workflow Execution | Static, pre-defined scripts | Adaptive, real-time automation |
| Context Awareness | Limited memory retention | Maintains long-term user context |
| Proactivity | User-driven interactions | AI-driven recommendations |

Beyond-RAG: From Answer Generation to Action Execution
Traditional retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) models focus on retrieving the most relevant answer from a knowledge base. However, AI agents go beyond RAG, integrating task execution into customer interactions.
While LLM-based chatbots (e.g., ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini) enhance conversation quality, they lack the ability to autonomously trigger workflows or execute tasks. Instead, they require external APIs or orchestration layers to turn conversational outputs into actionable workflows.
For instance, an LLM-based chatbot can:
- Provide detailed, context-aware answers to user queries.
- Generate dynamic responses rather than predefined script-based answers.
- Cannot independently trigger backend actions without API integrations.
By contrast, AI agents are designed for end-to-end task execution. Instead of simply answering:
"How do I reset my password?"
An AI agent can:
- Verify user identity through security protocols.
- Automatically reset the password.
- Notify the user of the action taken.
This bridges information retrieval with workflow execution, making AI agents true digital assistants rather than static responders.
AI agents achieve this through:
- AI-Driven API Calls – Agents directly interact with external systems (e.g., CRMs, payment processors).
- Task Prioritization Models – AI assigns workflow priorities based on customer urgency.
- Adaptive Learning – AI agents continuously improve based on historical interactions.
![(a) Flowchart of the workflow in Fig. 3a, illustrating 10 possible customer scenarios [Step 1, E2E pipeline], along with an example of user information, system information, and the success criteria for one scenario [Steps 2 and 3].](https://blog.premai.io/content/images/2025/03/Screenshot-2025-03-13-alle-14.24.28-1.png)
Real-World Use Cases: AI Agents in Automated Workflows

AI Agents in Customer Service
A large e-commerce company implemented AI-driven workflow automation to handle customer refunds. The AI agent:
- Detected refund requests based on user conversations.
- Checked past transactions in real time.
- Approved refunds instantly or escalated cases as needed.
This led to 50% faster response times and reduced customer service workload.
Future of AI-Driven Workflow Automation
- Proactive Issue Resolution – AI will anticipate problems and offer solutions before users report issues.
- Enterprise-Wide AI Orchestration – AI will integrate across multiple platforms, handling voice, email, and chat.
- Autonomous Customer Service Agents – Future AI systems will resolve complex service requests without human involvement.
Selecting the Right AI Solution
As businesses explore AI-powered customer support, the choice between traditional chatbots and advanced AI agents depends on multiple factors, including the complexity of interactions, scalability, and automation needs. Chatbots remain suitable for structured, repetitive tasks such as FAQs and transactional interactions, offering a cost-effective, rule-based approach. However, as customer expectations evolve, AI agents have become the preferred choice for enterprises requiring dynamic, context-aware responses, workflow automation, and integration with business-critical systems.
Unlike static chatbots, AI agents leverage real-time decision-making, adaptive learning, and API-driven automation to enhance efficiency and user experience. The shift toward autonomous customer service is evident, with AI agents increasingly capable of handling multi-platform interactions across chat, email, and voice channels while proactively resolving customer issues before escalation. As AI technology advances, businesses should focus on scalable AI solutions that seamlessly integrate with existing workflows, ensuring long-term adaptability and continuous improvement in customer engagement. Investing in AI agents today positions organizations for the future of AI-driven customer experience, reducing operational costs while maximizing automation-driven efficiency.
References:








