14 Best Self-Hosted Claude Alternatives for AI and Coding in 2026
Compare 14 self-hosted Claude and Claude Code alternatives with open-source AI platforms, coding tools, and model runners you can deploy on your own infrastructure.

Claude is one of the best AI assistants available. Claude Code raised the bar for agentic coding workflows. But sending proprietary data and source code to Anthropic's servers isn't an option for every team.
Compliance requirements, data sovereignty rules, or just a preference for control over your AI stack can all push you toward self-hosted alternatives.
The good news: open-source tools have caught up fast. Some are chat interfaces. Some are Claude Code alternatives built for VS Code or the terminal. Others are the model runners that power everything underneath.
This list covers all three categories. Each tool is something you can deploy on your own infrastructure, with no vendor lock-in and no usage limits beyond your hardware.
What to Look for in a Self-Hosted Claude Alternative
Before picking a tool, think about what you actually need from it.
1. Model quality and AI reasoning. Claude Opus and Sonnet set a high bar. Self-hosted tools let you run models like Llama, Mistral, Qwen, and DeepSeek. None of them are Claude, but the gap is narrowing with every release.
2. API compatibility. Most tools in this list support OpenAI-compatible endpoints. That means swapping backends without rewriting your integration code.
3. Deployment flexibility. Docker, Kubernetes, bare metal, desktop app. The best tools meet you where your infrastructure already lives.
4. Coding features. If you're replacing Claude Code specifically, look for VS Code extensions, agentic workflows, code review, and terminal-based automation.
5. Fine-tuning and customization. Chat UIs give you a private AI assistant. But if you need models trained on your own data, you need a platform that supports fine-tuning and evaluation.
6. Enterprise readiness. Multi-user access, SSO, role-based permissions, audit logs. These matter once you move past solo use.
Quick Comparison Table
1. Prem AI
Full-stack enterprise AI platform with autonomous fine-tuning, evaluation, and self-hosted deployment.
License: Commercial (free tier available) · Best for: Enterprise teams needing a complete private AI platform · Runs on: AWS VPC, on-premises, Kubernetes · Models: 30+ base models including Mistral, Llama, Qwen, Gemma
Prem AI is the only tool on this list that handles the full lifecycle: dataset preparation with automatic PII redaction, fine-tuning with knowledge distillation, evaluation with LLM-as-a-judge scoring, and one-click deployment. It's built for teams that need more than a chat interface.
The autonomous fine-tuning system runs up to 6 concurrent experiments and picks the best-performing model automatically. Swiss headquarters and zero data retention architecture make it a fit for regulated industries with strict compliance requirements.
If your goal is running models customized to your domain, not just chatting with a generic LLM, this is where you start. Enterprise teams can book a demo here.
2. Open WebUI
The most popular self-hosted AI chat interface, with 50K+ GitHub stars and a large community.
License: Open source (custom license with branding requirement)
Best for: Teams wanting a polished ChatGPT-like experience on their own servers Runs on: Docker, Kubernetes
Models: Any model via Ollama or OpenAI-compatible API
Open WebUI pairs well with Ollama for a completely offline setup. The interface feels familiar if you've used ChatGPT. Built-in RAG with citations, multi-user support with role-based access control, and a growing plugin ecosystem round it out.
Where it gets interesting: Python function calling built into the tools workspace, voice and video chat support, and a model builder for creating custom agents. The main limitation is that it's a frontend. You still need a model runner like Ollama or vLLM behind it, and RAG quality depends heavily on how you tune the pipeline.
3. AnythingLLM
All-in-one workspace that bundles chat, document Q&A, and AI agents in a single package.
License: MIT (open source)
Best for: Small teams or individuals who want RAG and agents without stitching together multiple tools
Runs on: Desktop app, Docker
Models: Ollama, LM Studio, OpenAI-compatible APIs
AnythingLLM stands out for its workspace model. You create separate workspaces for different projects, each with its own documents, models, and agent configurations. Upload PDFs, markdown files, or sync a GitHub repo, and the built-in RAG engine makes that content available in your conversations.
Multi-user roles, webhook integrations for connecting to tools like n8n, and an embeddable chat widget for websites are nice touches. The desktop app runs without Docker, which lowers the setup bar significantly. Watch for occasional stability issues on some platforms and note that the cloud version doesn't publish pricing.
The latest version (1.7.2) added NPU support for Snapdragon devices, giving a roughly 30% boost in RAG operations on compatible hardware.
4. LibreChat
Multi-model chat UI that looks and feels almost identical to ChatGPT.
License: Open source (MIT)
Best for: Teams wanting a unified interface across many AI providers
Runs on: Docker (requires MongoDB, PostgreSQL, MeiliSearch)
Models: OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Mistral, Ollama, and dozens more
LibreChat supports more AI providers out of the box than any other self-hosted option. Claude, GPT, Gemini, local models via Ollama, and everything in between. The artifacts feature renders React components, HTML, and Mermaid diagrams inline, similar to what you'd get in claude.ai.
AI agents with MCP tool integration, a code interpreter supporting Python, JavaScript, Go, Rust and more, and a prompt library builder with variables and dropdowns. The 2025 roadmap includes a hosted version and chain-of-thought agents using mixture-of-agents architecture.
The downside: deployment involves 5 separate services (LibreChat, RAG-API, MongoDB, MeiliSearch, PostgreSQL), which makes the setup heavier than alternatives like Open WebUI. And the permissions system is still catching up to enterprise needs.
5. Jan.ai
Offline-first desktop app for running local models with zero configuration.
License: Apache 2.0 (open source)
Best for: Individuals who want a private Claude alternative on their laptop
Runs on: Desktop (Windows, Mac, Linux)
Models: Downloads from HuggingFace, built-in model explorer
Jan keeps things simple. Download the app, pick a model from the built-in hub (it tells you which ones your hardware can handle), and start chatting. No Docker. No terminal commands. No API keys.
The interface is modern and polished compared to older local AI tools. Regular updates bring new models and features. The project has 40K+ GitHub stars and active development.
Where it falls short: the community is smaller than Ollama or Open WebUI, documentation is less comprehensive, and file upload support is still experimental. If you need multi-user features or team management, look elsewhere.
6. PrivateGPT

Document Q&A tool built for privacy. Ask questions about your files without anything leaving your machine.
License: Apache 2.0 (open source)
Best for: Teams with sensitive documents who need local-only document analysis
Runs on: Self-hosted server
Models: Local models via various backends
PrivateGPT does one thing well: it lets you chat with your documents privately. Upload files, ask questions, get answers grounded in your content. If your use case is "I need an AI that reads our internal docs and stays on-prem," this is the most focused option.
It's not trying to be a full chat platform. No multi-user management, no agent workflows, no plugin ecosystem. That narrow scope is both its strength and limitation. For teams in healthcare, legal, or finance where document confidentiality is non-negotiable, the simplicity is a feature.
7. Cline
Open-source agentic coding assistant for VS Code with 4M+ installs.
License: Apache 2.0 (open source)
Best for: Developers wanting a Claude Code alternative with deep agentic workflows in VS Code
Runs on: VS Code extension
Models: Any model (cloud or local via Ollama/LM Studio)
Cline is the most popular open-source Claude Code alternative for developers. The plan, review, run workflow lets you describe a task, review the proposed changes, and approve execution step by step. It can edit files, run terminal commands, browse your local dev server, and connect to external services via MCP tools.
The model-agnostic approach means you can pair it with local models for near-zero marginal cost, or route to cloud APIs when you need stronger AI reasoning. Cline raised $32M in funding in 2025 and the extension is expanding to JetBrains and Neovim.
Where it falls short: long coding sessions accumulate API costs if you're using cloud models. And lower-quality local models degrade output significantly, especially on large codebases. Treat it like a junior developer who needs supervision.
8. Continue.dev
Open-source VS Code and JetBrains extension for building your own AI coding assistant.
License: Apache 2.0 (open source)
Best for: Teams standardizing an open-source AI coding stack across editors
Runs on: VS Code, JetBrains
Models: Any model (local or cloud)
Continue is less of a ready-made agent and more of a framework for building your own coding assistant. Point it at Ollama or LM Studio for fully local AI coding assistance, or connect to hosted models. Customize prompts, configure tool integrations, and define workflows that match how your team works.
The cross-IDE support (VS Code and JetBrains) gives it an edge over Cline for teams that aren't standardized on one editor. Solo tier is free. Team tier is $10/dev/month.
The tradeoff: it requires more upfront configuration than tools that work out of the box, and local model support needs sufficient VRAM to run smoothly.
9. Aider
Terminal-based AI coding assistant that's Git-aware from the ground up.
License: Apache 2.0 (open source)
Best for: Terminal-first developers who want precise, auditable code edits
Runs on: CLI tool
Models: Local and cloud models
Aider reads your repo, makes edits, and commits changes with sensible messages. It understands Git history and diffs, which makes it better at surgical refactors in large codebases than tools that treat code as flat text.
Pair it with a local model through Ollama for fully private coding assistance. The CLI-driven workflow won't appeal to everyone, but developers who live in the terminal appreciate the precision. It doesn't try to be an agent that takes over your whole workflow. It's a pair programmer that proposes changes and lets you accept or reject them.
10. Tabby
Self-hosted autocomplete server. Think GitHub Copilot, but on your own infrastructure.
License: Open source
Best for: Startups and teams needing team-wide coding assistance without per-seat API costs
Runs on: Docker, bare metal (supports consumer-grade GPUs)
Models: StarCoder, CodeLlama, Qwen, and other code-focused LLMs
Tabby is self-hosted autocomplete for your whole team. Set up the server, connect the VS Code extension, and every developer gets inline code suggestions powered by your own hardware. No per-seat fees, no code leaving your network.
The Answer Engine feature lets developers ask questions and get answers grounded in your internal documentation and codebase. Repository-level context awareness, LDAP authentication, and team analytics make it enterprise-ready. With 32K+ GitHub stars, it's one of the more mature self-hosted coding tools available.
The limitation is scope. Tabby is focused on completions and code Q&A, not agentic coding workflows. For that, pair it with Cline or Aider.
11. Ollama
The simplest way to run LLMs locally. One command. Powers half the tools on this list.
License: MIT (open source)
Best for: Anyone who wants to get local models running in under a minute
Runs on: Mac, Linux, Windows
Models: Llama, Mistral, Gemma, DeepSeek, Qwen, Phi, and hundreds more
ollama run llama3 and you're chatting with a local model. That's the pitch, and it delivers. Ollama handles model downloads, quantization, and serving behind an OpenAI-compatible API endpoint. Open WebUI, AnythingLLM, Cline, and Continue all use it as a backend.
If you're exploring self-hosted AI for the first time, start here. It takes the complexity out of running language models locally.
The limitation is that Ollama is an engine, not an interface. You'll want to pair it with a chat UI or coding tool from this list.
12. LocalAI
OpenAI-compatible drop-in replacement that runs on consumer hardware, no GPU required.
License: MIT (open source)
Best for: Teams wanting OpenAI API compatibility on CPU-only infrastructure
Runs on: Docker, bare metal
Models: GGML, GGUF, GPTQ format models
LocalAI exposes an OpenAI-compatible API, meaning any tool or codebase that talks to OpenAI can point at LocalAI instead. No code changes needed. It supports text generation, embeddings, image generation, and audio transcription.
The CPU-only option makes it accessible on machines without dedicated GPUs, though response times are slower. Good for automation pipelines where latency matters less than cost and privacy. For production workloads where throughput depends on your hardware, GPU acceleration is still recommended.
13. vLLM
High-throughput inference engine for production workloads. What you use when Ollama isn't enough.
License: Apache 2.0 (open source)
Best for: Production deployments needing maximum inference performance
Runs on: Linux with NVIDIA/AMD GPUs
Models: Most HuggingFace models
vLLM uses PagedAttention for efficient memory management, which translates to higher throughput and lower latency than most other serving frameworks. If you're running AI models at scale for an internal API or product feature, vLLM is the production-grade option.
Prem AI supports deploying fine-tuned models to vLLM for self-hosted inference.
The tradeoff: vLLM is an inference engine, not a user-facing tool. It requires more setup and ops knowledge than Ollama. No chat UI, no plugin system. Pure serving performance.
14. LM Studio
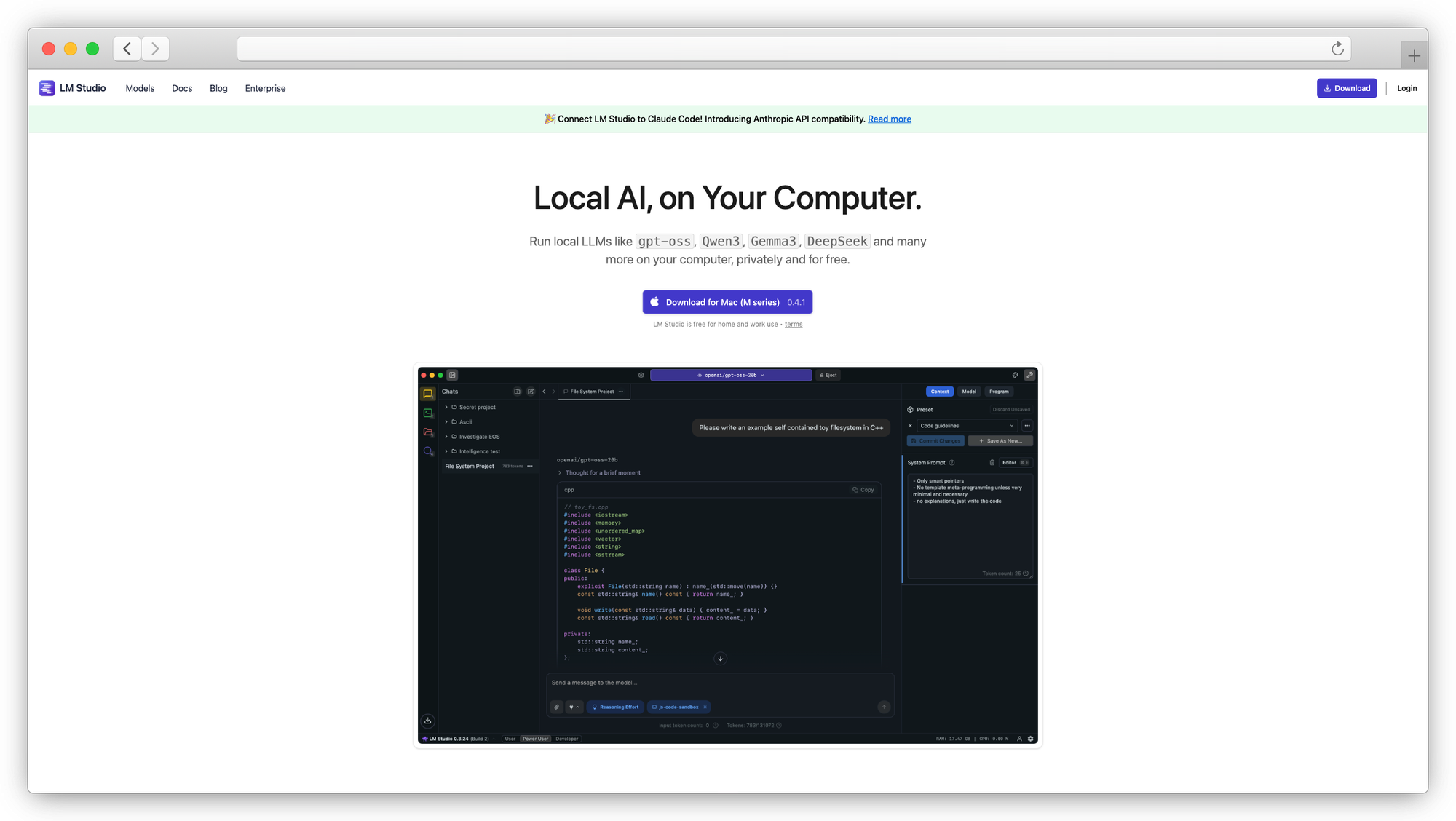
Desktop app for downloading, running, and chatting with local models through a GUI.
License: Proprietary (free for personal use)
Best for: Developers who want a visual way to browse and test local models
Runs on: Desktop (Windows, Mac, Linux)
Models: Downloads from HuggingFace
LM Studio gives you a searchable interface for HuggingFace models, shows which ones fit your hardware, and lets you chat or expose a local API endpoint. It's a good starting point for evaluating which open-source models work for your use case before committing to a deployment stack.
The local API server means other tools (Cline, Continue, Open WebUI) can connect to models running in LM Studio. Not designed for team or production use, but useful for prototyping and exploration.
How to Pick the Right Self-Hosted Alternative
Start with your use case and work backward.
Just exploring local AI? Install Ollama, pull a model, then add Open WebUI or LM Studio as a frontend. You'll be up and running in minutes.
Need a private chat interface for your team? Open WebUI or LibreChat. Both support multiple users, model switching, and RAG. LibreChat has a wider provider list. Open WebUI has a simpler deployment.
Looking for an open-source Claude Code alternative for agentic coding? Cline for VS Code. Aider for the terminal. Continue if you need JetBrains support. Add Tabby for team-wide self-hosted autocomplete.
Building production AI pipelines with custom models? Prem AI for fine-tuning and evaluation, then deploy to vLLM for self-hosted inference.
Regulated industry with strict compliance requirements? Prem AI's Swiss jurisdiction and cryptographic verification, combined with on-premises deployment, handles data sovereignty at the infrastructure level. For a deeper look, see the GDPR-compliant AI chat guide.
FAQ
1. Can self-hosted models match Claude's AI reasoning?
The honest answer: not yet for the most complex tasks. Claude Sonnet and Opus still lead on nuanced reasoning, long-context analysis, and coding quality. But open-source models like Llama 3.1 405B, DeepSeek V3, and Qwen 2.5 72B come close for many practical workflows. And fine-tuned smaller models can outperform larger general models on domain-specific tasks.
2. What hardware do I need to run local models?
For 7B parameter models: 8GB VRAM (an RTX 3060 or M1 Mac works). For 13B-30B models: 16-24GB VRAM. For 70B+ models: multiple GPUs or quantized versions with 48GB+ VRAM. CPU-only inference is possible through LocalAI but expect slower response times. Start small with Ollama and a 7B model to test before investing in hardware.
3. Are there usage limits with self-hosted alternatives?
No vendor-imposed caps. When you self-host, the only limits are your hardware capacity and whatever API budget you set for cloud model routing. That's the core appeal. No usage limits, no per-seat pricing surprises, and no dependency on a provider's rate limiting.
4. Can I use these as a Claude Code alternative for coding?
Yes. Cline gives you deep agentic coding workflows in VS Code with a plan, review, run loop. Continue works across VS Code and JetBrains as a configurable AI coding assistant. Aider handles Git-aware edits from the terminal. Tabby is self-hosted autocomplete for your whole team. All of them support local models through Ollama, so your code never leaves your machine.
Conclusion
Most of these tools solve one piece of the puzzle. Chat UIs give you a private interface. Coding tools replace Claude Code in your IDE. Model runners get open-source LLMs running on your hardware.
Prem AI is the one platform that covers the full lifecycle. Upload your data, fine-tune a model on your domain, evaluate it against your own benchmarks, and deploy to your infrastructure. No piecemeal setup. No stitching together five different open-source projects and hoping they work together.
If you're past the experimentation phase and need AI models that actually know your business, with compliance baked in at the infrastructure level, get started with Prem AI or book a demo with the team.
